Healing from childhood trauma is a journey. Traumatic events can have lasting effects in the way your brain functions and the way your body responds to stress. Different forms of psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy, have been shown to effectively help people process and cope with trauma.
However, while therapy can be a powerful tool, it isn’t the only way to recover. Other coping mechanisms and practices can help people process and understand their trauma on the path toward healing.
It’s important to note that these concepts aren’t necessarily replacements for professional help. If you’re struggling with suicidal thoughts, call or text 988 to reach the Suicide and Crisis Lifeline in the US. You can also browse these mental health resources for immediate response.
Key Takeaways
- Healing from childhood trauma involves self-awareness, mindfulness, and healthy coping mechanisms.
- Building a support network provides validation and understanding, and practicing self-compassion facilitates personal growth and healing.
- If your experience with trauma isn’t improving, contact a professional. Self-care practices can complement ongoing therapy.
Understanding Child Trauma and Its Impact
Child trauma refers to experiences that cause intense physical and psychological stress reactions. These traumatic events can have a lasting adverse effect on a person’s ability to function and overall well-being.
When a child experiences a traumatic event, it can lead to significant changes in the systems that are involved in the body’s stress response, such as the cortisol and norepinephrine systems.
One of the key players in the stress response is the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. In individuals who have experienced childhood trauma, the HPA axis can become dysregulated, leading to irregularities in the body’s stress response.
Brain imaging studies have also shed light on the impact of childhood trauma on brain function. Individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) often show specific circuitry changes in the brain, highlighting the far-reaching effects of trauma on neurological functioning.
Healing From Childhood Trauma
Healing from childhood trauma is a complex and deeply personal journey. Therapy is a valuable tool in this process, but developing healthy coping strategies can help people manage their trauma response and move toward healing.
Self-Awareness
Understanding trauma triggers and thought patterns can help people manage their emotions and behavioral responses.
A trigger refers to something that reminds you of a traumatic experience and causes fear, panic, or another negative response. Triggers can range from sounds and smells to a piece of clothing or a specific place or situation.
Developing self-awareness requires a conscious effort to observe your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors when you feel triggered.
For example, you might recognize that your body feels unsafe, and then intervene by practicing deep-breathing exercises, engaging in positive self-talk, or calling a friend to help process the emotion.
Engaging in Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Participating in activities that bring joy and relaxation can significantly reduce stress and promote overall well-being. These healthy coping mechanisms help individuals to channel their energy and emotions in a positive direction, in search of solace and purpose, rather than falling into negative thoughts and emotions.
Here are some examples of healthy coping mechanisms that can aid in the healing process:
- Engaging in Hobbies: Pursuing hobbies can be a source of comfort and fulfillment. Whether it’s gardening, playing an instrument, or cooking, indulging in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment can help individuals navigate the healing journey.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical exercise not only benefits physical health but also contributes to emotional well-being. Activities such as walking, cycling, yoga, or dancing release endorphins, boost mood, and alleviate stress, promoting a healthier mindset.
- Exploring Creative Outlets: Creativity can be a powerful tool for healing and self-expression. Engaging in creative outlets like painting, writing, photography, or crafting allows individuals to explore their emotions, find solace, and gain a sense of accomplishment.
By incorporating these healthy coping mechanisms into their daily lives, individuals can establish a stable foundation for healing, resilience, and personal growth.
Building a Support Network
Healing from childhood trauma requires a strong support network. Surrounding yourself with trusted friends and family members who offer understanding and empathy can provide a sense of validation and support throughout your healing journey.
Having someone to talk to and share experiences with can be immensely helpful in processing your emotions and navigating the challenges that arise along the way. Whether it’s a close friend, a sibling, or a caring relative, their presence and listening ear can make a significant difference in your healing process.
When building your support network, consider reaching out to those who you trust and feel comfortable confiding in. Look for individuals who possess qualities such as empathy, compassion, and the ability to truly understand your experiences. By surrounding yourself with such individuals, you can create a safe space to share your thoughts, emotions, and concerns, fostering a sense of understanding and connection.
Remember, healing from childhood trauma is not a journey you have to navigate alone. Building a support network of trusted friends and family members can provide the understanding and support you need to heal and grow.
Practicing Self-Compassion
Practicing self-compassion is a vital aspect of the healing process. It involves being gentle and kind to yourself, nurturing a sense of self-acceptance and self-love. Here’s why it matters:
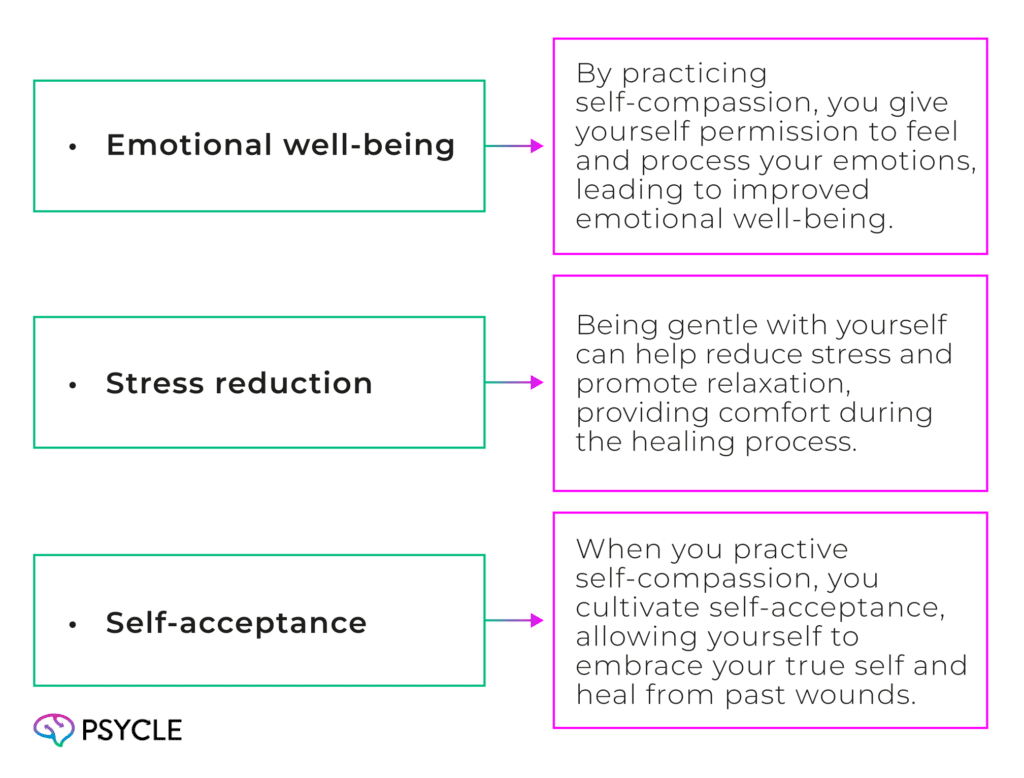
Remember, healing is a journey, and self-compassion plays a significant role in that journey. By being gentle with yourself and practicing self-care, you can foster healing, self-acceptance, and personal growth.
Conclusion
It’s absolutely possible to heal from childhood trauma. Therapy is an important tool in your recovery toolkit, but other practices can help you learn how to manage your emotions, stress responses, and behaviors in a healthy way.
FAQs
Is It Possible to Heal From Childhood Trauma Without Therapy?
It’s possible. However, working with a professional therapist can help people develop healthy coping strategies and process difficult emotions and memories that are tailored to their needs.
What Are the Neurobiological Effects of Childhood Trauma?
Childhood trauma can have neurological effects on brain function and the stress response. It can lead to alterations in neurotransmitter and neurohormonal systems, such as cortisol and norepinephrine systems, which are involved in the stress response. Brain imaging studies have also shown specific circuitry changes in individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
How Can Practicing Self-Awareness and Mindfulness Aid in Healing From Childhood Trauma?
Practicing self-awareness allows individuals to gain insights into their emotional and behavioral responses, which is important in the healing process. Mindfulness, through practices like meditation and deep breathing exercises, helps individuals stay present and grounded.
What Role Do Healthy Coping Mechanisms Play in the Healing Process?
Engaging in healthy coping mechanisms, such as hobbies, exercise, and creative outlets, provides individuals with a sense of purpose and fulfillment, and it distracts from negative thoughts and emotions. These activities can help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Why Is Building a Support Network Essential in Healing From Childhood Trauma?
Building a support network allows individuals to seek understanding and empathy from trusted friends or family members. It provides a sense of validation and support, and having someone to talk to and share experiences with can help process emotions and navigate the healing journey.
How Does Practicing Self-Compassion Contribute to the Healing Process?
Practicing self-compassion involves being gentle with oneself and practicing self-care. It fosters self-acceptance and self-love, promotes emotional well-being and growth. Acknowledging that healing takes time and allowing oneself to feel and process emotions without judgment are key aspects of self-compassion.

