Childhood trauma can have long-lasting effects, causing people to feel constantly on edge and in a state of survival mode, even when there’s no danger present. However, it’s possible to overcome these challenges.
This article will explore the impact of trauma and how to heal and manage childhood trauma that leads to ongoing survival mode.
Key Takeaways
- Childhood trauma can manifest in various symptoms, including intrusive memories, anxiety, avoidance, and hypervigilance, which keeps individuals in a state of survival mode.
- Professional therapy, such as EMDR, CBT, psychodynamic therapy, somatic experiencing, and group therapy, provides tailored strategies for healing trauma and breaking free from survival mode.
- Establishing safety involves removing toxic relationships, ensuring physical safety, and surrounding oneself with supportive individuals to create a stable and secure environment conducive to healing.
- Practicing self-compassion is crucial in soothing heightened arousal and promoting emotional regulation. Techniques include mindfulness meditation, positive affirmations, self-care rituals, and treating oneself with kindness and understanding.
- Developing coping skills, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation, can activate the rest and digest parasympathetic mode, counteracting survival mode’s harmful effects and promoting overall well-being.
Acknowledge Your Past: Recognize the Trauma and Its Impact
The American Psychological Association (APA) defines trauma as “an emotional response to a terrible event like an accident, rape, or natural disaster.” It can result from any event a person finds physically or emotionally threatening or harmful and presents as a variety of symptoms, including:
- Intrusive memories and flashbacks to the event
- Depressed mood and anxiety
- Avoidance
- Difficulties in interpersonal relationships
- Sleep disturbances
Hypervigilance – the state of being highly alert to potential danger is a common effect of trauma. It develops as a coping mechanism to experiences in which an individual’s sense of safety has been shattered, and the brain’s threat detection system becomes overactive. This often manifests as feeling in a state of survival mode, even when there’s no danger around.
If such experiences occur in childhood, when the brain is most malleable, hypervigilance can occur well into adulthood. It can be difficult to overcome since this maladaptive coping mechanism can become deeply wired into the brain.
Nonetheless, with strong intentions, self-compassion, and therapeutic support, it’s possible to re-configure your nervous system and help the brain learn it no longer needs to be in survival mode.
Recognizing the trauma and its impact enables you to take control of your healing journey. It empowers you to seek the support and resources necessary to navigate the path toward emotional freedom. Remember, your past does not define you, but by the resilience and strength you possess as you confront and overcome the effects of childhood trauma.
Seek Professional Support: Therapists Can Provide Tailored Strategies for Healing
Professional therapists who specialize in trauma have the knowledge and experience to help individuals explore the depths of their trauma, understand its impact on their lives, and develop effective coping mechanisms.
Through therapy sessions, individuals can gain insights and strategies specifically designed to manage the effects of the trauma and break free from survival mode.
Therapy provides a safe and supportive environment for individuals to express themselves openly without fear of judgment, allowing them to process their experiences, emotions, and thoughts.
Here are some of the different approaches to healing trauma in therapy and helping get people out of survival mode
- EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing):
- EMDR is a therapy that helps individuals process traumatic memories by using bilateral stimulation, such as eye movements or tapping, to alleviate distress associated with those memories. It aims to reprocess the traumatic experiences, reducing their emotional impact, including ongoing survival mode.
- CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy):
- CBT is a talk-based structured therapy focused on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It helps individuals develop coping strategies for situations that remind them of the traumatic event, helping them learn to escape unnecessary survival mode.
- Psychodynamic Therapy:
- Psychodynamic therapy explores how unconscious thoughts and past experiences influence current behaviors and emotions, including those related to trauma. Through exploration of unconscious conflicts and relational dynamics, individuals gain insight into their trauma and develop healthier ways of coping.
- Somatic Experiencing:
- Somatic Experiencing (SE) focuses on the physiological sensations and bodily responses associated with trauma, aiming to release pent-up energy from traumatic experiences. Other body-based techniques can be learned to help calm the nervous system and come out of fight-or-flight mode.
- Group Therapy:
- Group therapy provides a supportive environment where individuals with similar experiences, such as trauma survivors, come together to share their stories, learn coping skills, and gain validation and support from peers. Through interaction and feedback within the group, members can develop a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation while learning from others’ experiences.
The effectiveness of different trauma therapies depends on factors such as the nature of the trauma, individual differences, cultural considerations, and a person’s existing support systems. Therapists must consider these contextual factors to choose the most appropriate therapy and tailor treatment to the individual’s needs and circumstances.
Benefits of Seeking Professional Support
- Validation and understanding: Therapists provide a non-judgmental space where individuals can feel validated and understood. They help individuals realize their experiences and emotions are valid, which can be incredibly empowering.
- Tailored strategies for healing: Therapists focus on addressing the specific impacts of childhood trauma and creating a path toward growth and recovery.
- Emotional support and guidance: Therapists provide ongoing emotional support, guidance, and encouragement throughout the healing process. They equip individuals with tools and techniques to navigate challenges, ultimately fostering emotional well-being.
Establish Safety: Create a Stable, Secure Environment
To help overcome trauma, it’s important to establish a safe and secure environment while embarking on your healing journey. This is important for helping your nervous system re-learn that it’s no longer under threat.
Remove Toxic and Abusive Relationships
If you find yourself in toxic or abusive relationships, take steps to distance yourself from these harmful connections, whether it be through setting boundaries or, in some cases, cutting ties completely. Remember, your emotional well-being must always come first.
Ensure Your Physical Safety
Creating a safe environment also means taking the necessary steps to ensure physical safety without being so overly cautious that it impacts your well-being. This may involve taking extra precautions to secure your home and finances, being careful when sharing personal information, and being knowledgable about how to protect yourself, such as learning martial arts.
Surround Yourself with Supportive and Nurturing People
Building a network of supportive and nurturing individuals can significantly contribute to your emotional well-being and create a sense of security. Surround yourself with people who uplift and validate you, whether friends, family members, or support groups. Investing in relationships built on trust and understanding will provide the stability you need to heal.
Practice Self-Compassion: Treat Yourself with Kindness and Understanding
Self-compassion encourages individuals to acknowledge and validate their feelings without judgment, fostering a sense of safety and acceptance within themselves.
By cultivating self-compassion, individuals can gradually learn to soothe their heightened arousal, recognize when they are safe, and respond to triggers with self-care and understanding rather than fear or avoidance.
This shift in perspective allows for a gentler approach to managing hypervigilance and facilitates the process of healing from trauma by promoting self-awareness, resilience, and emotional regulation.
Here are some tips for practicing self-compassion:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Engage in mindfulness practices to become aware of your thoughts and emotions without judgment, allowing yourself to experience them fully.
- Positive Affirmations: Use positive self-talk and affirmations to counter negative self-perceptions and cultivate self-compassion.
- Self-Care Rituals: Prioritize activities that nurture your physical, emotional, and mental well-being, such as exercise, adequate sleep, healthy eating, and relaxation techniques.
- Self-Kindness: Treat yourself with the same kindness and understanding you would offer to a close friend facing similar challenges or struggles.
Develop Coping Skills: Learn Techniques to Manage Stress and anxiety
Survival mode is often associated with the body’s fight-or-flight response, which is when the nervous system’s sympathetic branch is activated.
This physiological state primes the body to either confront the threat (fight) or flee from it (flight), leading to increased heart rate, heightened arousal, and a focus on immediate survival needs.
However, it’s possible to activate the rest and digest parasympathetic mode, which is the opposite of survival mode, through simple techniques that promote relaxation and calmness.
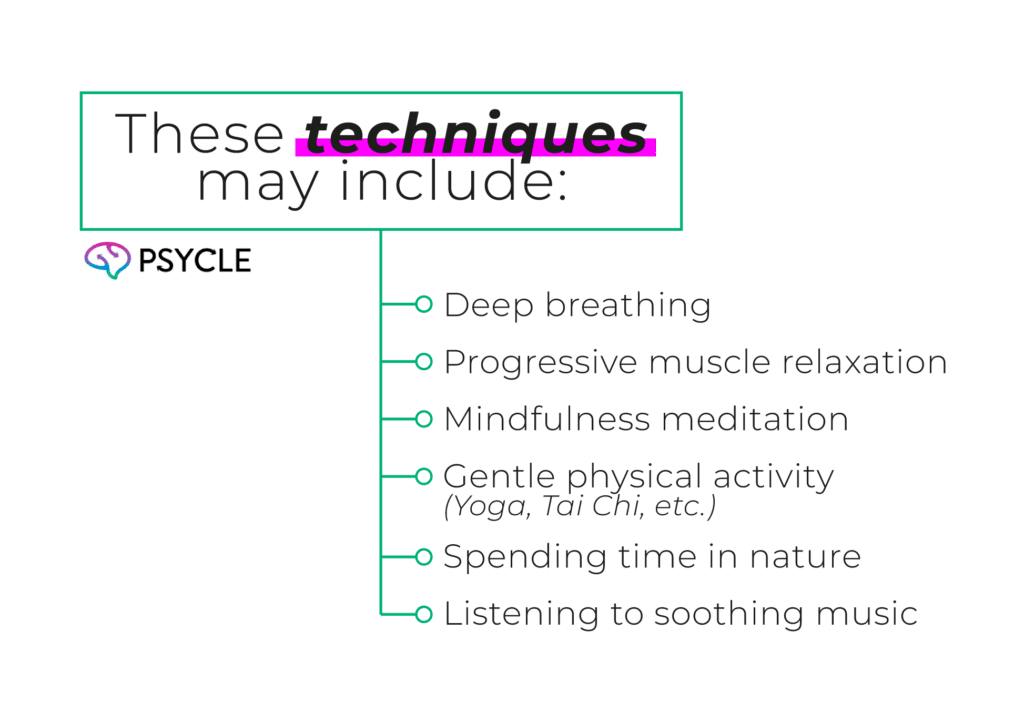
If you feel like you may be entering survival mode unnecessarily or know you’re encountering situations in which survival mode is often triggered, you can try using these techniques to help overcome fight-and-flight mode.
Adopting relaxation as part of your daily routine can promote overall better health by decreasing the harmful physical and psychological effects of stress.
FAQs
How Does Childhood Trauma Impact a Person’s Life?
Childhood trauma, such as abuse, neglect, or witnessing violence, can have a significant impact on a person’s life. It can lead to the development of survival mode, characterized by heightened stress, anxiety, hypervigilance, and difficulty forming healthy relationships.
What Are Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)?
Adverse childhood experiences include emotional and physical abuse, neglect, household substance abuse, parental separation or divorce, and more. These experiences can affect individuals from all socioeconomic backgrounds and races and contribute significantly to negative adult physical and mental health outcomes.
How Can Professional Support Help in Overcoming Survival Mode Triggered by Childhood Trauma?
Seeking professional support from therapists specializing in trauma and childhood trauma can provide tailored strategies for healing. They can help individuals explore their trauma, address underlying issues, and develop coping mechanisms to manage the effects of the trauma.
How Can I Establish Safety in My Life?
To establish safety, it is important to create a stable and secure environment both physically and emotionally. This may involve removing yourself from toxic or abusive relationships, ensuring physical safety, and surrounding yourself with supportive and nurturing people.
Why Is Self-Compassion Important in Healing From Childhood Trauma?
Self-compassion is critical in healing from childhood trauma as it involves treating yourself with kindness, understanding, and acceptance. Practicing self-care activities, engaging in hobbies, practicing mindfulness, and seeking support from friends or family members can promote well-being and contribute to the healing process.

