EMDR therapy is gaining popularity as more people become interested in what this innovative therapy has to offer. However, many aren’t too sure what EMDR actually is, and falsely think it’s some kind of hypnosis. This article will outline some of the core differences between EMDR and hypnosis, explaining what each therapeutic approach involves, how they work, and what to expect from a course of sessions.
Key Takeaways
- EMDR and hypnosis both involve focused attention, but they are not the same.
- EMDR reprocesses traumatic memories using bilateral stimulation and structured phases.
- Hypnosis helps change habits, reduce stress, or manage pain through guided suggestion.
- EMDR has strong scientific support for trauma recovery.
- Hypnosis works best for behavioral and emotional regulation.
- Choosing between them depends on your goals and personal response to each method.
What Is EMDR Therapy?
EMDR stands for Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing. It’s a structured type of psychotherapy that helps people process and heal from trauma using bilateral stimulation. This involves activating both sides of the brain simultaneously using sensory stimulation, such as tapping, sounds, and eye movements.
Psychologist Francine Shapiro developed EMDR in the late 1980s after noticing that side-to-side eye movements reduce distress linked to painful thoughts. The therapy was initially developed for treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) but has later found use in other issues such as depression, anxiety, panic attacks, and grief.
Today, EMDR is backed by scientific studies and is recognized by major organizations like the American Psychological Association and the World Health Organization as an effective treatment for trauma-related disorders.
Because of this recognition, many insurance companies include EMDR in their mental health benefits for certain conditions.
How EMDR Works
EMDR therapy follows an eight-phase process.
You and your therapist start by building trust and learning coping strategies to regulate your nervous system. This preparation helps you to feel safe and ready for the therapeutic process. You’ll also identify specific memories or symptoms you want to work on.
Once ready, you’ll recall the memory or symptoms while the therapist guides you through bilateral stimulation techniques. This typically includes moving the eyes side-to-side or playing sounds from one ear to another through noise-cancelling headphones. You’ll be asked to focus on positive beliefs to help reprogram the trauma’s effects.
The overall goal isn’t to eliminate harmful memories, but to alter how your nervous system responds to them. You’ll have a check-in after the repromming sessions to see what changes have been made, and whether you need further sessions.
Sessions usually last between 60 and 90 minutes. The overall therapy may take several weeks or months, depending on your condition, life circumstances, and goals.
Why People Have EMDR Therapy
EMDR therapy has several uses, but the most common include
- PTSD and complex PTSD
- Anxiety and depression linked to past events
- Grief or loss
- Emotional numbness or flashbacks
EMDR doesn’t require a detailed retelling of every part of the trauma, which makes it helpful for people who find talk therapy difficult.
What Is Hypnosis and Hypnotherapy?
Hypnosis is a state of deep relaxation in which you remain awake, but become less aware of your surroundings. In this state, you’re more open to suggestions, which are ideas or instructions to help you change thoughts, feelings, or behaviours.
Hypnosis has a long history, with evidence of ancient civilizations using hypnotic practices in rituals to heal the body and soul. In the 18th century, physician Franz Mesmer introduced the concept of “animal magnetism.” He believed that disease was caused by obstacles in the flow of fluids in someone’s body, which could be broken through trance states. This laid the groundwork for the development of modern hypnosis.
How Hypnosis Works
A typical hypnosis session starts with relaxation or guided imagery. A hypnotist, or hypnotherapist, will help you focus your attention through calm speech or gentle counting. Once you reach a relaxed state, the therapist gives suggestions designed to help you change thoughts or behaviors.
These suggestions might target habits like smoking, anxiety about public speaking, or physical discomfort. Some sessions use imagery, while others use direct verbal cues. You’re always aware and can choose to stop or shift focus at any time.
The number of hypnosis sessions will vary depending on the person’s goals and unique reactions. Some people report making significant changes after just one session.
Hypnosis vs. Hypnotherapy
Hypnosis describes the mental state itself, whereas hypnotherapy means using that state for therapeutic goals. Hypnotherapy is performed by a trained professional who helps you use hypnosis to manage symptoms or reach personal goals.
Why People Use Hypnosis
People often choose hypnosis or hypnotherapy to:
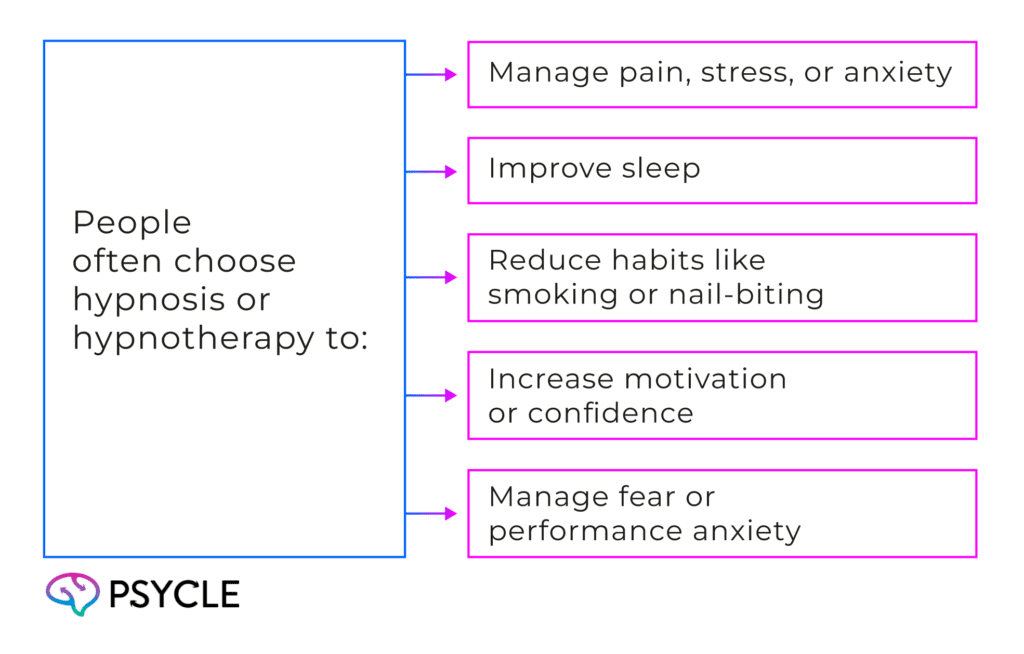
Like EMDR therapy, hypnosis is a clinically recognized form of mental health treatment. However, it’s not valued as a standalone treatment, but rather as an additional form of holistic treatment that is recommended alongside conventional therapy or medication. For this reason, it’s not typically covered through insurance.
Scientific Mechanisms: EMDR vs. Hypnosis
Both EMDR and hypnosis involve changes in attention, focus, and emotion. However, they differ in how they influence the brain and body.
The Science of EMDR Therapy
It’s not completely clear how EMDR therapy works in the brain, but there are several theories. Brain scans show that when the brain becomes synchronized, there is a decrease in activity of the amygdala—a region that responds to threat. This helps people process traumatic memories without feeling overwhelmed or distressed.
The brain state induced in EMDR is also similar to rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. REM is a sleep phase when the brain processes events and moves them into long-term memory stores. EMDR therapy may be working on similar mechanisms, bringing memories to the surface and re-processing them.
The Science of Hypnosis
Like EMDR therapy, the neuroscience of hypnosis remains largely hypothetical. However, studies using brain imaging show changes in the anterior cingulate cortex and prefrontal cortex — regions linked to focus and perception. In hypnosis, you may experience suggestions more vividly because your brain temporarily shifts how it evaluates reality.
Research also shows that hypnosis increases activation of the body’s parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), a branch of the nervous system that activates when someone feels safe.
Overlap and Differences
Both EMDR therapy and hypnosis use techniques to relax the nervous system, but the methods are different. EMDR therapy uses bilateral stimulation, whereas hypnosis uses guided imagery.
The goals of each therapy are also different. Both aim to help change thought and behaviour through changing someone’s brain state, rather than talking. However, EMDR focuses on changing symptoms related to past events, whereas hypnosis focuses on changing habits, mood, and thinking.
EMDR also follows a structured evidence-based protocol, whereas hypnosis is more varied.
Which Is Better: EMDR or Hypnosis?
No single therapy works best for everyone. Each method offers specific advantages depending on your goals and comfort level.
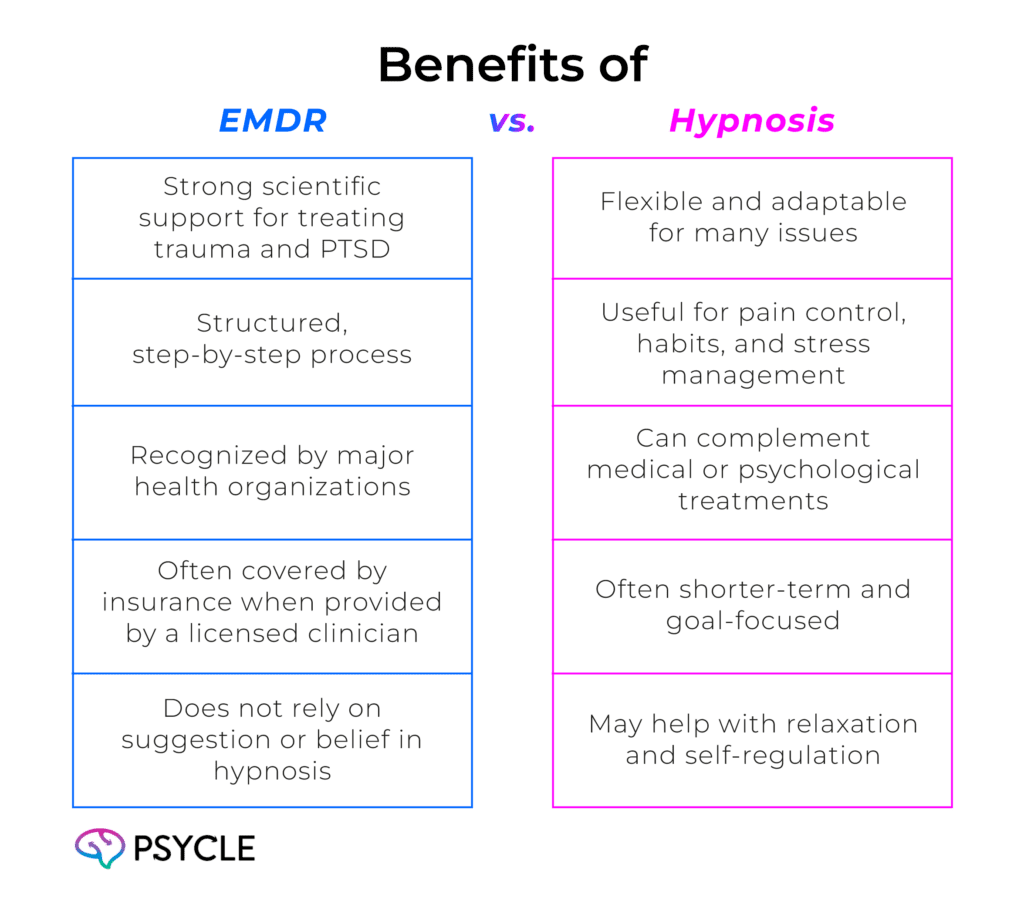
Limitations
EMDR may feel emotionally intense because it involves revisiting distressing memories. Hypnosis requires openness to suggestion and may vary in effectiveness depending on the person and the practitioner’s skill.
Both methods work best when you trust your therapist and feel safe in the process.
EMDR vs. Hypnosis: Which One Is Right for You?
You might choose EMDR if your main goal is to process trauma or disturbing life events that still affect you. EMDR is well supported for PTSD and emotional symptoms linked to specific memories. It helps when you want to feel less triggered and more in control of your reactions.
You might choose hypnosis if you want to manage stress, increase positive thinking, or change habits. Hypnosis focuses on behavior and mindset rather than memory reprocessing. It can also support medical care for pain, anxiety, or nausea.
If you’re unsure, talk to a licensed mental health professional or hypnotherapist. A therapist trained in both methods can help you decide based on your personal history and needs.
FAQs
Is Hypnosis Scientifically Validated?
Hypnosis has been studied for many decades and has scientific support for specific uses. Research shows it can help reduce pain, anxiety, stress, and some phobias. It is also used in medical settings for procedures or symptom management. However, its effectiveness can vary depending on the person, the skill of the therapist, and the goal of the treatment. Hypnosis is less standardized than EMDR, so results may differ from session to session.
Can I Be Retraumatized with EMDR?
EMDR is designed to safely process traumatic memories without retraumatizing you. The therapy uses structured steps and preparation to keep you grounded and ensure you’re ready before undergoing the EMDR techniques.
Some discomfort or emotional intensity can occur while recalling memories, but the therapist helps you manage it and returns you to a stable state before ending the session.
If someone who isn’t properly trained in EMDR therapy offers you some sessions, this could be more dangerous, as they may not know how to support you properly to prevent retraumatization.
Sources
- https://emdrassociation.org.uk/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6357291/

