Intrusive thoughts can be incredibly unsettling. They creep into our minds, unwelcome and disturbing. But what’s even more perplexing is how real they feel. These vivid and unwanted thoughts often trigger intense emotions, causing us to question our sanity. So, why do intrusive thoughts feel so real?
The answer lies in the way our brains process information. When faced with intrusive thoughts, our brains treat them as real threats, activating the amygdala, the fear center of the brain. This heightened brain activity leads to a heightened perception of danger, making the intrusive thoughts feel incredibly lifelike.
Furthermore, intrusive thoughts can blend with personal memories, tapping into deep-seated emotions and experiences. This connection intensifies their impact, reinforcing their sense of reality. Additionally, intrusive thoughts often reflect our deepest fears and anxieties, resonating with our most primal emotions. They may even tap into hidden desires or forbidden thoughts, further amplifying their impact.
Understanding the psychology behind why intrusive thoughts feel so real is essential for managing their impact on our mental well-being. By recognizing the nature of intrusive thoughts, understanding the brain processing involved, and addressing the connections to personal memories, fears, and desires, we can regain control over our thoughts and lead healthier lives.
Key Takeaways
- Intrusive thoughts feel real because our brains treat them as real threats, activating the fear center of the brain.
- These thoughts can blend with personal memories, intensifying their impact and reinforcing their sense of reality.
- Intrusive thoughts often reflect our deepest fears and anxieties, resonating with our most primal emotions.
- Understanding the psychology behind intrusive thoughts is crucial for managing their impact on our mental well-being.
- By recognizing their nature, addressing brain processing, and exploring personal connections, we can regain control over our thoughts.
The Nature of Intrusive Thoughts
Intrusive thoughts are unwelcome and often disturbing thoughts that can occur repeatedly and intrude into a person’s consciousness. These thoughts can involve various themes, such as harm, contamination, or uncertainty. They can feel extremely real and are often characterized by a sense of urgency and danger.
For individuals experiencing intrusive thoughts, it can be challenging to differentiate between these intrusive thoughts and actual reality. The vividness and intensity of these thoughts make them difficult to dismiss or ignore. They can consume a person’s attention and impact their emotions, leading to significant distress.
Understanding the nature of intrusive thoughts is crucial for addressing their impact on mental health and well-being. By gaining insight into why these thoughts occur and the factors that contribute to their intensity, individuals can develop effective strategies for managing them.
The Themes of Intrusive Thoughts
Intrusive thoughts can manifest in a variety of themes, although their specific content may vary from person to person. The following are common themes observed in intrusive thoughts:
- Harm-focused thoughts: Thoughts of causing harm to oneself or others
- Contamination-related thoughts: Fears of contamination or becoming infected, leading to excessive cleanliness rituals or avoidance behaviors.
- Uncertainty and doubt: Persistent doubts and uncertainties about everyday decisions, causing excessive rumination and anxiety.
- Sexual or taboo thoughts: Intrusive thoughts related to inappropriate or taboo subjects
These themes are not exhaustive, and intrusive thoughts can take many other forms. It is essential to recognize that even though these thoughts may feel real, they do not necessarily reflect the true desires, intentions, or character of the individual experiencing them.
Understanding the Impact
The intense realism of intrusive thoughts can have a profound impact on mental health and overall well-being. They can lead to heightened anxiety, depression, and impaired daily functioning. Individuals may develop avoidance behaviors to manage the distress caused by these thoughts, further exacerbating the impact on their quality of life.
Moreover, the persistent nature of intrusive thoughts can be emotionally exhausting, leading to increased stress and feelings of helplessness.
The Role of Brain Processing
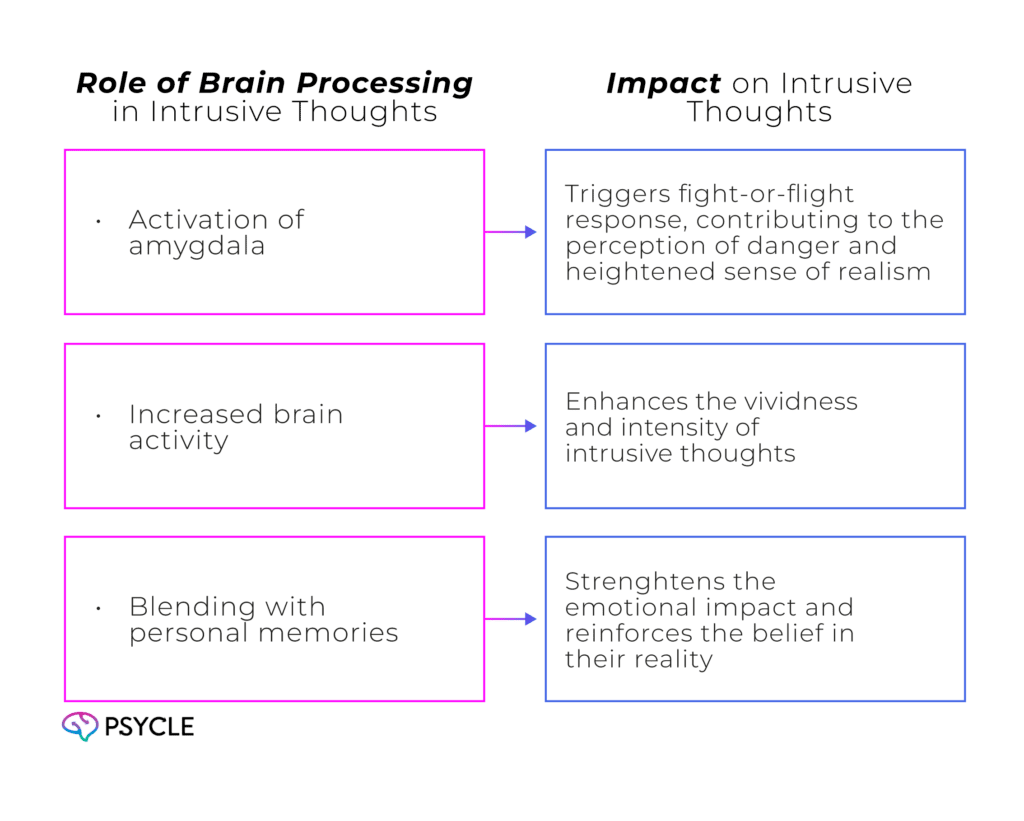
Research suggests that the brain processes intrusive thoughts in a similar way to real threats. The amygdala, the brain’s threat detection center, is activated, leading to the perception of danger and triggering a fight-or-flight response. This response is a survival mechanism designed to protect us from harm. However, in the case of intrusive thoughts, the brain is interpreting them as genuine threats, even if they are not based on real events or situations.
This heightened brain activity contributes to the vividness and realism of intrusive thoughts. As a result, intrusive thoughts can elicit strong emotional responses and contribute to the perception that they are immediate and imminent dangers.
Understanding the Fight-or-Flight Response
The fight-or-flight response, triggered by the amygdala, is a physiological reaction that prepares the body to either confront a threat or flee from it. This response causes various bodily changes, such as increased heart rate, heightened senses, and the release of stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
When the amygdala perceives a threat, it activates this response, even if the threat is only a thought. As a result, the brain’s processing of intrusive thoughts mirrors its response to real threats, leading to a heightened sense of their realism.
Dr. Samantha Martinez, a psychiatrist specializing in anxiety disorders, explains, “During the fight-or-flight response, the brain directs resources towards dealing with the perceived threat, which further reinforces the intensity and reality of intrusive thoughts.”
Understanding the role of brain processing in the experience of intrusive thoughts can provide valuable insights into their nature and why they feel so real. By recognizing the physiological processes involved, individuals can develop strategies to better manage and cope with intrusive thoughts.
The Connection to Personal Memories
Intrusive thoughts have a unique ability to intertwine with personal memories. This connection occurs because these thoughts often tap into deeply ingrained emotions and experiences, leveraging the brain’s tendency to associate them with personal moments.
The brain treats these thoughts as significant events, triggering intense emotions and a strong belief in their authenticity. This blending of intrusive thoughts and personal memories can be particularly challenging to manage, as it creates a powerful cognitive and emotional fusion.
The Role of Emotional Associations
One of the reasons why intrusive thoughts and personal memories become intertwined is the emotional associations they share. Personal memories have the ability to evoke strong emotions, whether positive or negative, due to the experiences and feelings attached to them.
Intrusive thoughts, with their often disturbing and unwanted nature, tap into these emotional associations. They exploit the brain’s tendency to link thoughts with significant emotional experiences, which intensifies their impact and reinforces their perceived reality.
Recognizing the Connection
Recognizing the connection between intrusive thoughts and personal memories is crucial for effectively managing their impact. By understanding that intrusive thoughts can hijack emotionally charged memories, individuals can develop strategies to untangle the fusion and regain control over their thoughts.
Therapy techniques such as cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy can help individuals separate intrusive thoughts from personal memories.
By challenging distorted beliefs and engaging in controlled exposure to triggering stimuli, individuals can gradually replace the emotional associations between intrusive thoughts and personal memories with healthier and more accurate perceptions.
Strategies for Managing Intrusive Thoughts
When it comes to managing intrusive thoughts, there are several strategies that individuals can employ to regain control over their thinking patterns. These strategies can help alleviate the intensity and frequency of intrusive thoughts, promoting improved mental well-being.
Here are some effective approaches:
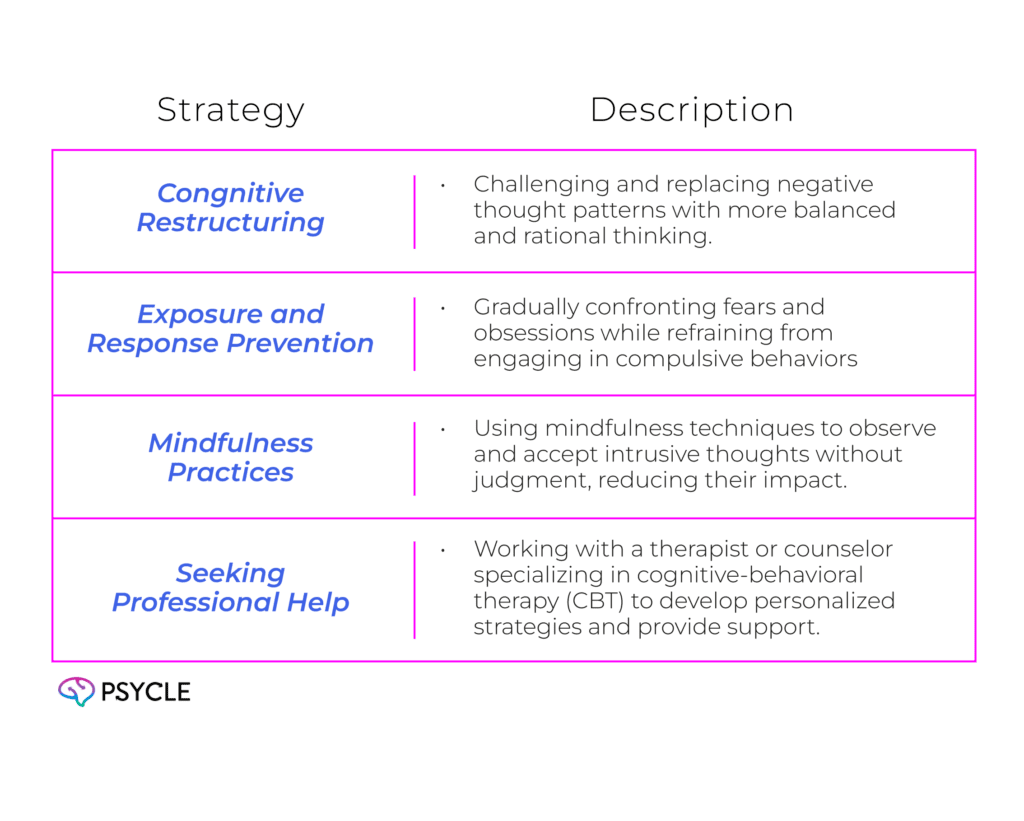
1. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Techniques
Cognitive restructuring and exposure and response prevention are commonly used CBT techniques for managing intrusive thoughts. Cognitive restructuring involves challenging and changing negative thought patterns, while exposure and response prevention focuses on gradually confronting and resisting the urge to engage in compulsive behaviors triggered by intrusive thoughts.
2. Mindfulness and Grounding Exercises
Mindfulness exercises, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help individuals develop a present-moment awareness that reduces the power of intrusive thoughts. Grounding exercises, such as focusing on the senses or engaging in physical activities like walking or stretching, can also help distract from and diminish the impact of intrusive thoughts.
3. Seeking Professional Help
For individuals struggling with intrusive thoughts, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide invaluable guidance and support. A trained mental health professional can assist in developing personalized strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
Click the banner below to get access to a professional and start your online therapy journey!

By incorporating these strategies into their daily lives, individuals can gradually gain control over intrusive thoughts and improve their overall quality of life. It’s important to remember that managing intrusive thoughts is an ongoing process, and it may take time to find the strategies that work best for each individual.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Intrusive Thoughts
Intrusive thoughts can feel incredibly real and significantly impact an individual’s mental well-being. Understanding the psychology behind the realism of these thoughts is key to effectively managing them. By recognizing their nature, understanding brain processing, and addressing connections to personal memories, fears, and desires, individuals can regain control over their thoughts.
It is important to remember that taking control of intrusive thoughts is a process. Through therapy and the implementation of effective strategies, individuals can gradually reduce the impact of intrusive thoughts and improve their overall mental well-being.
FAQs
What are Intrusive Thoughts?
Intrusive thoughts are unwelcome and often disturbing thoughts that can occur repeatedly and intrude into a person’s consciousness.
Why Do Intrusive Thoughts Feel So Real?
Intrusive thoughts can feel incredibly real because the brain treats them as real threats, leading to a heightened feeling of their reality.
How Does the Brain Process Intrusive Thoughts?
Research suggests that the brain processes intrusive thoughts in a similar way to real threats, activating the amygdala, the brain’s threat detection center, and triggering a fight-or-flight response.
How Do Intrusive Thoughts Blend with Personal Memories?
Intrusive thoughts can blend with personal memories because they often tap into deeply ingrained emotions and experiences, intensifying their emotional impact and reinforcing their sense of reality.
Are Intrusive Thoughts Linked to Individual Fears and Desires?
Yes, intrusive thoughts are often linked to individual fears and desires, reflecting a person’s deepest anxieties and tapping into hidden desires or forbidden thoughts.
What Strategies Can Help Manage Intrusive Thoughts?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, mindfulness exercises, and seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor are effective strategies for managing intrusive thoughts.
How Does Therapy Help in Managing Intrusive Thoughts?
Therapy plays an important role in managing intrusive thoughts by providing individuals with tools, techniques, and coping mechanisms to challenge and change negative thought patterns, as well as exploring the underlying causes of intrusive thoughts.
How Can I Take Control of Intrusive Thoughts?
By understanding the nature of intrusive thoughts, the brain processing involved, addressing the connection to personal memories, fears, and desires, seeking therapy, and adopting strategies for managing intrusive thoughts, individuals can take steps to regain control over their thoughts and improve their mental well-being.

