Nail biting, or onychophagia, is a common habit that affects people of all ages. It may seem like a simple habit, but it can show signs of deeper psychological issues, like anxiety. Knowing how nail biting relates to anxiety is key to tackling these problems.
Onychophagia is a type of body-focused repetitive behavior, or BFRB, disorders. These habits can cause physical and mental problems, such as damaged nails and skin infections, and social issues.
Key Takeaways
- Nail biting, or onychophagia, is a common body-focused repetitive behavior (BFRB) that can be indicative of underlying psychological and psychiatric conditions.
- Nail biting is often associated with anxiety disorders and other mental health issues, suggesting a potential connection between this habit and anxiety.
- Understanding the relationship between nail biting and anxiety is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of these conditions.
- A comprehensive approach involving physical, psychological, and behavioral interventions is often necessary to address nail biting and its underlying causes.
- Early intervention and multidisciplinary treatment can help individuals with nail biting and anxiety disorders improve their overall health and well-being.
Introduction to Nail Biting
Definition and Prevalence
Nail biting, or onychophagia, is when people bite their nails often. It affects about 20-30% of people, especially kids from ages 10 to puberty, with rates up to 45%.
As people get older, they bite their nails less. But some start or keep doing it as adults. Students in college often bite their nails more, showing how stress can lead to this habit.
Nail Biting and Psychological Factors
Nail biting is a common habit linked to deep psychological reasons. It’s often seen as a way to reduce tension and manage emotions. Some people bite their nails without thinking, while others do it on purpose to ease stress or boredom.
Studies reveal that those who bite their nails are more likely to have anxiety. This shows how complex the link between nail biting and psychological issues is. The habit can offer a sense of relief or control for those dealing with stress or tension.
Nail biting can also be a way to control emotions. It acts as a distraction or release, helping to manage psychological factors that affect behavior.
Knowing what drives nail biting is key to finding ways to stop it. By tackling the underlying causes, people can find better ways to cope. This could help them stop biting their nails for good.
Psychiatric Comorbidities of Nail Biting
Nail biting might seem like a simple habit, but it could be linked to deeper mental health issues. Studies have looked into how nail biting and psychiatric disorders are connected. They found a complex relationship between the two.
Anxiety Disorders and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
The connection between nail biting and OCD or anxiety is not always easy to see. But, many studies suggest that a lot of nail biters also these conditions. In fact, up to 25% of those with chronic nail biting also have OCD or anxiety. But, it’s key to remember that not everyone with nail biting has these conditions.
Nail biting is also linked to other mental health issues, like ADHD, oppositional defiant disorder, separation anxiety, enuresis, or bedwetting, and tic disorder. These findings show that nail biting and mental health are more connected than we thought. We need to learn more about this connection.
But not everyone who bites their nails is anxious or has a mental health issue. It could just be a habit or a nervous habit. Some might do it out of boredom or to keep their nails short.
If nail biting is causing problems, hurting your body, or showing other signs of anxiety, getting help is a good idea. A mental health expert can offer treatments like cognitive-behavioral therapy or habit-reversal training. These can help manage nail biting and deal with the emotional or psychological reasons behind it.
Etiology and Contributing Factors
The causes of nail biting are complex and not fully known. Yet, research points to a mix of genetic factors and environmental influences playing a part. This mix likely affects how people develop this habit.
Family history is key in understanding nail biting. If a family member bites their nails, you’re more likely to do it too. This hints at a genetic predisposition. It means some people might be more prone to it because of their genes.
But it’s not just genes. Environment also matters. Kids might start biting nails by watching others do it. This can make the habit stick.
Stress and anxiety also add to nail biting. Some people bite their nails to cope with these feelings. Though it might offer short-term relief, it doesn’t solve the deeper issues.ail biting has many causes —genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and psychological factors. Knowing these factors is key to stopping and preventing this habit.
Quality of Life and Stigma
Severe nail biting can deeply affect a person’s quality of life. It often leads to psychological distress and physical damage. Those who bite their nails feel ashamed and have tried many times to stop.
This habit makes people feel anxious and self-conscious. It can make it hard to make friends and do everyday tasks. They might hide their hands a lot, causing more psychological distress and hurting their quality of life.
The stigma around nail biting stops some from getting help. People might not want to talk about it because they fear being judged.
- Severe nail biting can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life
- Psychological distress and physical damage can lead to social anxiety and self-consciousness
- Stigma surrounding nail biting can be a barrier to seeking help and support
We need to work on the quality of life and stigma of nail biting. By spreading awareness, offering good treatments, and being kind, we can help people overcome their struggles. This way, they can improve their quality of life.
Personality Profiles and Behavioral Problems
Recent studies have shown a strong link between nail biting, personality, and behavior issues. A study used latent profile analysis to find four main personality types in children who bite their nails:
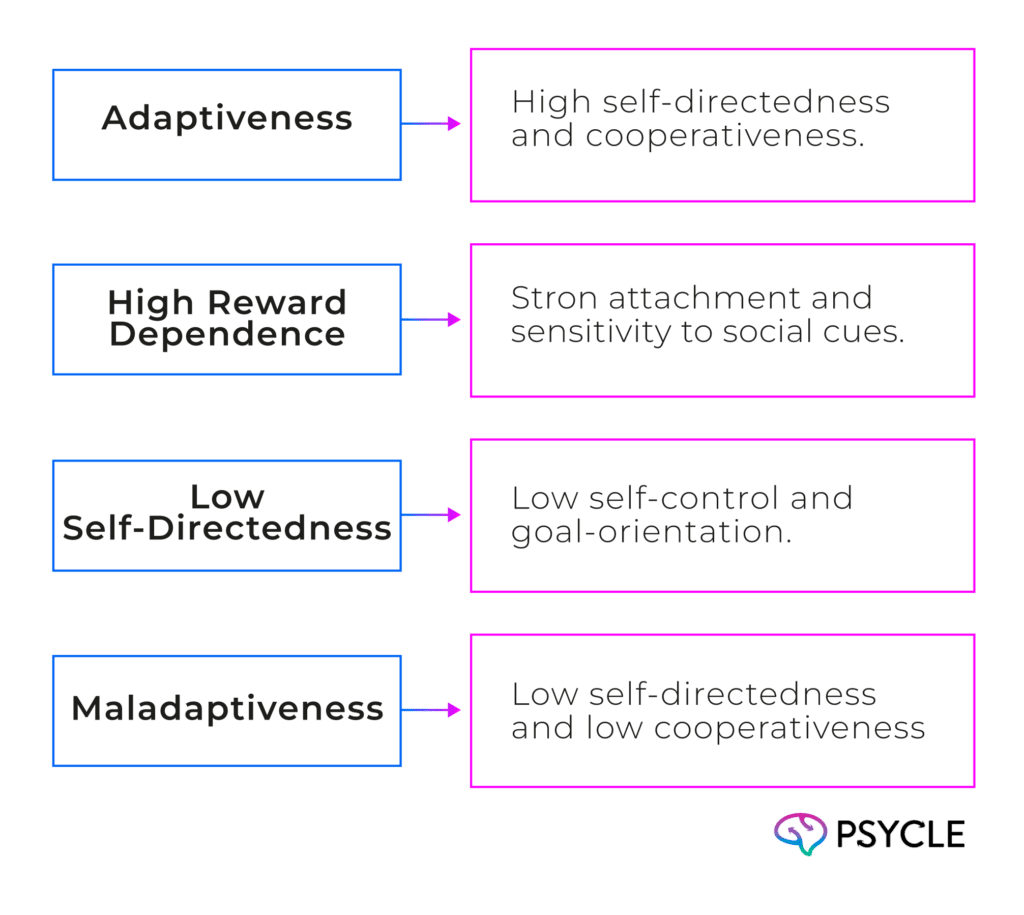
Children with ‘low self-directedness’ and ‘maladaptiveness’ were most likely to have behavioral problems. This was true even if they didn’t bite their nails a lot. So, when dealing with nail biting in kids, we should look at their personality profiles too.
Management and Treatment Options
Dealing with nail biting needs a mix of non-drug and drug treatments. Experts like dermatologists, internists, and psychiatrists work together. They look at the physical, mental, and behavioral sides of the issue.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
Non-drug treatments aim to change habits and behaviors. They include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to change negative thoughts and actions
- Habit reversal training to switch nail biting with better habits
- Manicures and nail polish to make biting less appealing
- Wearing gloves or bitter-tasting nail polish to deter biting
Pharmacological Interventions
Some people might need drug treatments for nail biting. These can help with the mental issues that cause it. Options include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for anxiety and obsessive thoughts
- Naltrexone to lessen the pleasure from biting
- Botulinum toxin injections to weaken nail-biting muscles
How well these treatments work varies by person and the severity of the nail biting. Using both non-drug and drug treatments together often works best. This approach helps manage the condition and improves life quality.
Importance of Early Intervention
Nail biting is often more than just a habit. It can show deeper psychological or behavioral issues. Spotting and tackling it early is key to stopping worse physical and mental problems. It also helps improve long-term results for those fighting nail biting.
Early action helps find and fix the real reasons behind nail biting. Treating issues like anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder early helps people find better ways to cope and stops the habit from getting worse.
Early help also prevents the harm nail biting can do to nails, skin, and teeth. These problems can hurt and lead to serious issues later, like more infections and bad looks. By acting early, people can avoid these issues and stay healthier.
Nail biting can also make people feel ashamed and alone, hurting their self-esteem and social life. Early prevention and treatment lead to better coping skills, a stronger self-image, and happier social life. This makes life better overall.
In short, the role of early intervention in dealing with nail biting is huge. By starting early, people can dodge serious physical and mental issues. They can also see better outcomes and live healthier, happier lives.
Conclusion
Nail biting, or onychophagia, is a complex habit often linked to anxiety and stress. It’s not the only sign of anxiety, but it’s often seen with other mental health issues like anxiety disorders and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Managing nail biting means tackling the deep-seated psychological reasons behind it. It’s important to start early to prevent long-term harm to both physical and mental health. Seeing nail biting as a sign of deeper emotional needs is key to helping people. Understanding how nail biting connects to anxiety and other factors helps people work towards better self-awareness and self-control. This leads to a more fulfilling life.
FAQs
How is Nail Biting Associated With Psychological Factors?
People often bite their nails to reduce tension and manage their feelings. It’s linked to stress and trouble controlling emotions.
What are the Contributing Factors to the Development of Nail Biting?
Genetics and environment play a big part in starting nail biting. Seeing others bite their nails can also lead to it.
How Do Personality Profiles Influence Nail Biting and Behavioral Problems?
Research found four personality types in child nail biters: ‘adaptiveness,’ ‘high reward dependence,’ ‘low self-directedness,’ and ‘maladaptiveness.’ Those with ‘low self-directedness’ and ‘maladaptiveness’ tend to have more behavioral issues, even if they don’t bite their nails a lot.
What are the Management and Treatment Options for Nail Biting?
To manage nail biting, a team of doctors like dermatologists and psychiatrists can help. They offer both non-medical and medical treatments.

