Childhood rejection can deeply affect our emotional health and how we see ourselves. But, with caring guidance and helpful strategies, we can move past these wounds. We can start a path of healing and growing personally.
This guide looks at how rejection in childhood affects us emotionally,how it can hurt our self-esteem, and what we can do to overcome it.
Key Takeaways
- Childhood rejection can deeply impact self-esteem, leading to chronic low self-worth, depression, and difficulties in forming healthy relationships. Individuals may develop avoidant or anxious attachment styles, which affect their ability to trust others and maintain intimacy in relationships.
- Healing from childhood rejection trauma often involves therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Mindfulness. These therapies help reframe negative thoughts, manage emotions, and develop healthier coping mechanisms, promoting personal growth and emotional resilience.
- Building supportive friendships and practicing self-compassion are crucial for overcoming childhood rejection. Engaging in activities that foster self-love and healthy coping strategies, such as mindfulness, journaling, and creative expression, can help rebuild self-esteem and foster emotional healing.
Understanding the Impact of Childhood Rejection
Childhood rejection refers to the experience of being made to feel unworthy and unwanted during childhood. It can manifest in various forms, including social exclusion, bullying, neglect, or emotional unavailability from parents.
We often think of childhood rejection in terms of parental or caregiver rejection. However, there are other forms of rejection, including:
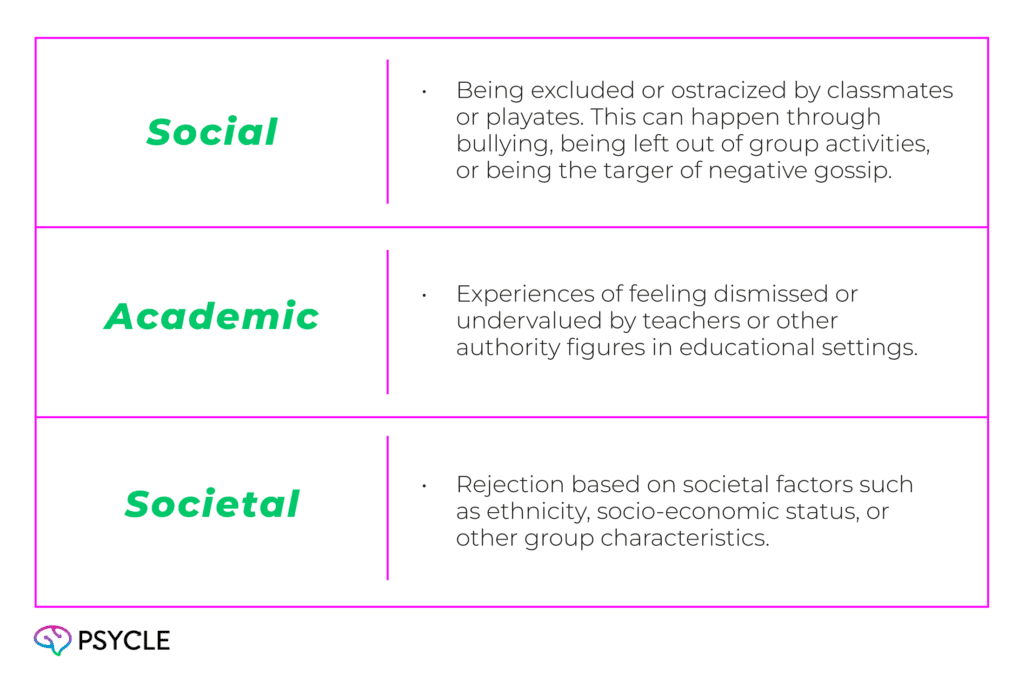
Children are particularly vulnerable to the long-term effects of rejection because their brains are still developing, making them highly sensitive to negative experiences. Moreover, it’s during these early years that people establish a sense of self and identity, and their place within society.
Emotional Consequences and Self-esteem Issues
Rejection can cause children to develop low self-esteem that carries through into adulthood. People rejected during childhood may feel worthless, which is a major risk factor for depression. They may also feel lonely by not having a notable value within society. This can impact someone’s work life, as they may feel uninspired or motivated to contribute to a profession.
Moreover, negative feelings associated with low self-esteem could cause someone to develop self-neglect, and not take care of their physical and emotional wellbeing, further hindering psychological problems.
Someone may also develop unhealthy ways to manage their negative thoughts, such as problematic drinking and drug-taking. One study from Turkey found adults who were emotionally neglected during childhood have a greater risk of substance abuse.
Relationship Consequences
Rejection during childhood can also hinder someone’s ability to form relationships. Attachment styles are concepts introduced by psychologist John Bowlby in 1958. They describe patterns of bonding and relationship behaviors formed during childhood.
Rejection trauma can lead to avoidant attachment, in which individuals learn to rely on themselves and suppress their emotional needs. This is characterized by being aloof or detached in relationships, and being uncomfortable with closeness and emotional intimacy.
Childhood rejection trauma can also lead to anxious attachment, in which individuals become overly dependent on others for validation and fear abandonment. This is characterized by clinginess, possessiveness, and heightened sensitivity to any signs of rejection or neglect.
Recognizing the Signs of Childhood Rejection Trauma
Healing from childhood rejection trauma starts with spotting the signs and patterns that stay with us into adulthood. Knowing these signs helps people start fixing the issues and growing personally and resiliently.
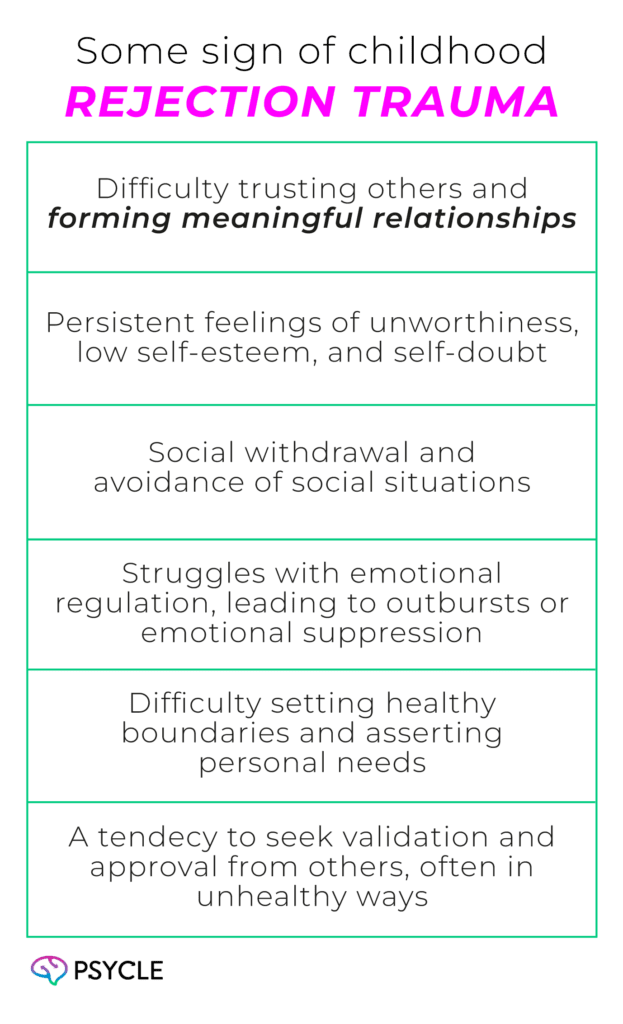
Identifying Emotional Scars and Behavior Patterns
Childhood rejection leaves deep emotional scars that affect our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Some signs of signs of childhood rejection trauma are:
Seeking Professional Help and Therapy
Getting help from professionals can greatly aid in healing from childhood rejection trauma. Professional help for rejection trauma offers support and guidance. It helps you deal with the tough feelings and challenges from those early days.
The Role of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a key therapy for dealing with childhood rejection trauma. It helps people spot negative thoughts and reprogram them. CBT also involves goal-setting and identifying practical strategies to help clients cope with negative thinking.
Exploring Mindfulness and Other Therapeutic Approaches
There are more therapeutic approaches that can help too.
Mindfulness-based practices teach people to live in the now, understand yourself better, and accept yourself more. Mindfulness also allows you to recognise thoughts without becoming attached to them. This allows people to notice thoughts around low self-worth but feel separate from them, and avoid spirals of rumination.
Eye movement desensitization and reprogramming therapy (EMDR) involves the use of guided eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation (like taps or tones) to help clients reprocess and integrate memories of rejection. This therapy can help people understand the root feelings of low-self worth, so when they occur, they can be recognised as a product of childhood, rather than taking them at face value.
Family Constellations Therapy (FCT) is a group therapy where participants may re-enact various family members, creating a living representation of the family system. This can allow someone to re-experience and address feelings of unlove and rejection in their family.
It’s important to pick a therapy that feels right for you, and a therapist who you resonate with. With the right mental health professional, you can start a healing journey. This journey leads to growth and healing from childhood rejection.
Inner Child Work
Inner child work involves addressing and healing the emotional wounds of one’s younger self by reconnecting with and nurturing the inner child—the part of oneself that holds past experiences and feelings.
This therapeutic approach helps overcome childhood rejection trauma by allowing individuals to revisit and reprocess painful memories with a compassionate, adult perspective. By validating and comforting the inner child, individuals can address and challenge negative core beliefs formed during childhood.
Inner child work may be conducted in a formal therapy session. You can also try some techniques yourself, such as:
- Writing compassionate letters to your younger self
- Visualizing your younger self and saying words of well-wishing to them
Building Self-Compassion and Self-Love
Healing from childhood rejection means changing how we see and treat ourselves. By practicing self-compassion and self-love, we can start to beat the negative thoughts and low self-esteem from back then.
Building self-love means loving and accepting ourselves fully, no matter what. It’s about seeing our true value and worth and replacing the harsh voice inside with a kinder one.
Here are some practical techniques for building self-love:
Daily Affirmations
- Write and recite 3-5 positive affirmations about yourself each morning.
- Use affirmation apps or sticky notes to keep them visible.
Self-Care Routine
- Set aside 30 minutes each day for activities that relax or rejuvenate you, like reading, taking a bath, or a hobby.
- Create a self-care checklist and track your activities.
Gratitude Journal
- Write down 3 things you’re grateful for each day, including personal achievements or qualities.
- Review your journal weekly to reinforce positive aspects of yourself.
Physical Activity
- Incorporate at least 20 minutes of exercise into your daily routine, like walking, yoga, or dancing.
- Choose activities that you enjoy and that make you feel good.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Healing from childhood rejection trauma is more than just acknowledging the pain. It’s key to learn healthy ways to deal with negative feelings and control your emotions. By using practical strategies, you can help yourself heal and become stronger when faced with tough times.
Techniques for Managing Negative Emotions
Learning to handle negative emotions is a big part of healing from childhood rejection trauma. Here are some helpful techniques:
- Mindfulness Practices: Mindfulness exercises like deep breathing, meditation, or body scans make you more aware of your thoughts and feelings. This lets you watch them without judging yourself.
- Journaling: Writing down your thoughts and feelings is a strong way to process and release emotions. Try free-form writing or structured prompts in your journal.
- Creative Expression: Activities like painting, drawing, or music let you express and deal with emotions in a healthy way.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise, such as yoga, walking, or swimming, helps control your emotions, lowers stress, and boosts your overall health.
It might take some time and trying different things to find the best coping strategies. Be kind to yourself as you try out various methods and see what suits you best.
Healing Through Relationships and Social Support
Healing from childhood rejection trauma is powerful when we build strong relationships and a supportive network. Healing through relationships, social support, supportive friendships, and chosen family changes how we recover from trauma.
The Importance of Supportive Friendships
Having good, supportive friends in adulthood is key for overcoming childhood rejection trauma. Healthy friendships allow us to feel supported and wanted.
Good friends are those who are happy for our successes, communicate with us honestly, respect our boundaries and support our personal growth. These are people we want to keep in our life and reciprocally support. However, this desire should come from a place of love, and not fear of further rejection.
Importantly, good friends are people that bring us joy.
If you’re looking to make new friends, you could try joining a social activity group for a hobby or passion you feel particularly interested about. Finding people with similar interests is a great starting point for lasting friendships.
Embracing Personal Growth and Resilience
Healing from childhood rejection trauma means growing and being resilient.
Conclusion
Recovery requires a mix of steps, like getting professional help, being kind to ourselves, and finding healthy ways to cope. By digging into why we feel the way we do, we can start to heal. This leads us to love ourselves more and become resilient and overcome the impact of childhood rejection trauma.
FAQs
How Can I Recognize the Signs of Childhood Rejection Trauma?
Adults who faced rejection as kids might find it hard to trust others or connect with people. They might pull away from social situations or struggle with feeling good about themselves. Spotting these signs can help them understand and work on healing.
What Types of Therapy Can Help With Healing from Childhood Rejection Trauma?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps change negative thoughts and teach better ways to cope. Trauma-focused therapy, such as EMDR, can also help you recognise the root of your feelings of self-worth, helping you better deal with and move past them.
What are Some Healthy Coping Mechanisms for Managing the Challenges of Childhood Rejection Trauma?
Mindfulness, journaling, and creative activities can help you deal with your feelings and emotions. They can also make you stronger when facing tough times.
What Practical Strategies Can I Implement to Heal From the Emotional Wounds of Childhood Rejection Trauma?
Using trauma-informed journaling, working with your inner child, and somatic practices can help you deal with your feelings and trauma. These methods can help you feel safe and trust others again.

