The psychological benefits of psychedelic and non-psychedelic mushrooms have been recognized throughout history. Contemporary research into their therapeutic potential has also grown over the past decade.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different types of mushrooms and their impact on mood, cognition, and capacity to treat mental health disorders.
Key Takeaways
- Mushrooms, both psychedelic and non-psychedelic, have shown potential benefits for mental health.
- Psilocybin-assisted therapy with magic mushrooms has demonstrated significant and long-lasting relief from symptoms of depression.
- Non-psychedelic mushrooms like lion’s mane have been associated with anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects.
- It is crucial to consider safety, legality, and individual circumstances when incorporating mushrooms into your mental health regimen.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the implications and potential therapeutic applications of mushrooms for mental well-being.

Overview of Mushrooms: Types and Varieties
Magic Mushrooms: Psychedelic Varieties
Magic mushrooms contain the psychoactive compounds psilocybin, psilocin, and baeocystin. In the brain, these compounds interact with proteins that normally respond to the chemical messenger serotonin, evoking a series of chemical events that can markedly change someone’s psychological state.
Common effects include:
- Altered sensory perception – including the perception of time
- Visual hallucinations – often a kaleidoscopic overlay
- Elevated mood and ‘bliss states’
- Confusion and disorientated thinking
- Paranoia and anxiety
- Enhanced emotions
Psilocybe cubesis are perhaps the most commonly used magic mushroom species worldwide. There are a variety of strains within this species, such as Golden Teachers and Penis Envy mushrooms, that mycologists and psychonauts have artificially bred to have different potencies, effects, and physical characteristics. Beyond cubensis, other popular magic mushroom species include:
- Psilocybe semilanceata, commonly known as “liberty caps”
- Psilocybe cyanesens, commonly known as “wavy caps”
- Psilocybe azurenscens
- Psilocybe mexicana, commonly known as “Mexican mushrooms”
- Panaeolus cyanescens
The spiritual and healing use of magic mushrooms has been recognized for centuries across Mesoamerica. For instance, the Mazatec–the native people of Northern Oaxaca, Mexico–regard the Psilocybe mexicana mushrooms as sacred and use them in ceremonies to help heal spiritual, emotional, and physical illnesses.
Globally, magic mushroom ceremonies have grown in popularity in recent years, with a marked rise the number of retreat centers offering healing mushroom experiences. Since magic mushrooms remain illegal in most countries worldwide, many of these ceremonies and retreats operate underground or in a legal grey area, raising concerns about the lack of regulatory oversight.
In contemporary research, psilocybin–the active ingredient in magic mushrooms–is also becoming increasingly recognized as a therapeutic tool.
Clinical trials have demonstrated psilocybin, alongside therapy, can help treat various mental health disorders, including:
- Depression,
- Anxiety associated with end-of-life disorders
- Substance abuse disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Eating disorders
Legal access to psilocybin-assisted therapy is mostly restricted to clinical trials. However, last year, Australia legalized psilocybin therapy for depression, and Oregon state opened its first legal psilocybin treatment center, highlighting the shift in psilocybin’s legal landscape.
Non-Psychedelic Mushrooms: Culinary and Medicinal Varieties
Non-psychedelic mushrooms encompass a diverse range of species, each with its own unique flavors and potential health benefits. These mushrooms don’t contain naturally occurring psychedelic compounds but are valued for their culinary versatility and potential medicinal properties.
Popular medicinal mushrooms include:
- Ganoderma sichuanense (Reshi)
- Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane)
- Trametes versicolor (Turkey Tail)
- Cordyceps militaris (Cordyceps)
- Lentinula edodes (Shiitake)
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has recognized the value of mushrooms, such as Reishi and Lion’s Mane in health for thousands of years. In Ayurveda, India’s ancient medical practice, the use of certain mushrooms for medicinal purposes has also been described.
Many of these mushrooms are considered to be nootropics, which are substances used to enhance cognitive function, such as memory and concentration. Researchers are becoming increasingly interested in their potential to treat mood disorders, although the current evidence is limited.
Mental Health Benefits of Magic Mushrooms
Decreases Activation of the Default Mode Network (DMN)
The default mode network (DMN) is a network of brain regions active during rest, associated with a person’s sense of self. This network is thought to be responsible for rumination–repetitive, involuntary, and often distressing thoughts–and is thought to be overactive in mental health disorders, such as depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Brain scanning experiments show psilocybin can disrupt DMN activity. Researchers think this is one of the main mechanisms by which psilocybin can help treat psychological disorders.
Decreases Amygdala Reactivity
Amygdala reactivity refers to the responsiveness of the amygdala, a part of the brain associated with processing emotions, especially fear and stress, and high amygdala reactivity is often observed in those with PTSD, depression, and anxiety disorders. Psilocybin has been shown to decrease amygdala reactivity in healthy volunteers, highlighting a mechanism for its therapeutic effects.
Increases Cognitive Flexibility
Psilocybin can increase cognitive flexibility – the ability to adapt thought and behavior to changing situations and consider diverse perspectives. This effect may help disrupt rigid, negative thought patterns and help people change unhealthy habits and behaviors.
Enhancement Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy involves identifying, understanding, and overcoming psychological difficulties. Psilocybin can help people understand and process their traumas by increasing cognitive flexibility and emotional openness. During experiences, people may also encounter repressed memories and emotions, allowing them to come to the surface to be processed and released. Psychotherapists can guide this process and support patients to encounter challenging psychological material.
Mental Health Benefits of Non-Psychoactive Mushrooms
Increased Neuroplasticity
Several studies show mushrooms such as Lion’s Mane can increase neuroplasticity – the ability for the brain to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. The nootropic effects of mushrooms are thought to be explained by this effect. In the context of mental health, neuroplasticity is beneficial because it enables individuals to learn new coping mechanisms and recover from trauma.
Immune System Regulation
Many mushroom species help regulate the immune system, the body’s natural defense system. Immune system dysregulation can damage nerve cells and is thought to play a role in mental health disorders and well a neurodegenerative disease, such as Alzheimer’s or depression. By regulating immunity, mushrooms could help restore some of the brain damage implicated in these diseases.
Decreased Stress
Chronic stress is a major risk factor in mental health disorders, particularly depression. Reishi mushrooms are recognized for their ability to decrease stress and have been shown to regulate levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, meaning they could help play a preventative role in the onset of mental health disorders.
Comparisons: Psychedelic vs. Non-Psychedelic
Like other non-psychoactive medicinal mushrooms, psilocybin-containing mushrooms may also help increase neuroplasticity and regulate the immune system. However, their psychological effects appear to be most important for mental health benefits.
Several studies have shown mystical experiences induced by psilocybin are correlated with therapeutic outcomes in clinical trials, demonstrating the importance of altered consciousness in this healing modality.
Because non-psychoactive mushrooms only work through biological and not psychological mechanisms, they may be less effective in treating mental health. However, the psychedelic effects which may be useful in psilocybin’s mechanism, also pose a major risk.
Psychedelic experiences can be distressing and confusing and have long-term negative effects, especially when used in unsupported settings. For this reason, it’s essential to use psilocybin or magic mushrooms with the support of a trained mental health professional, especially if you’re dealing with a mental health disorder.
Though non-psychoactive mushrooms don’t carry the same psychedelic and legal risks, they do carry side effects. Therefore, if you’re planning to begin supplementing with any of these mushrooms, make sure you know the risks and also whether they interact with any medications or supplements you may be currently taking.
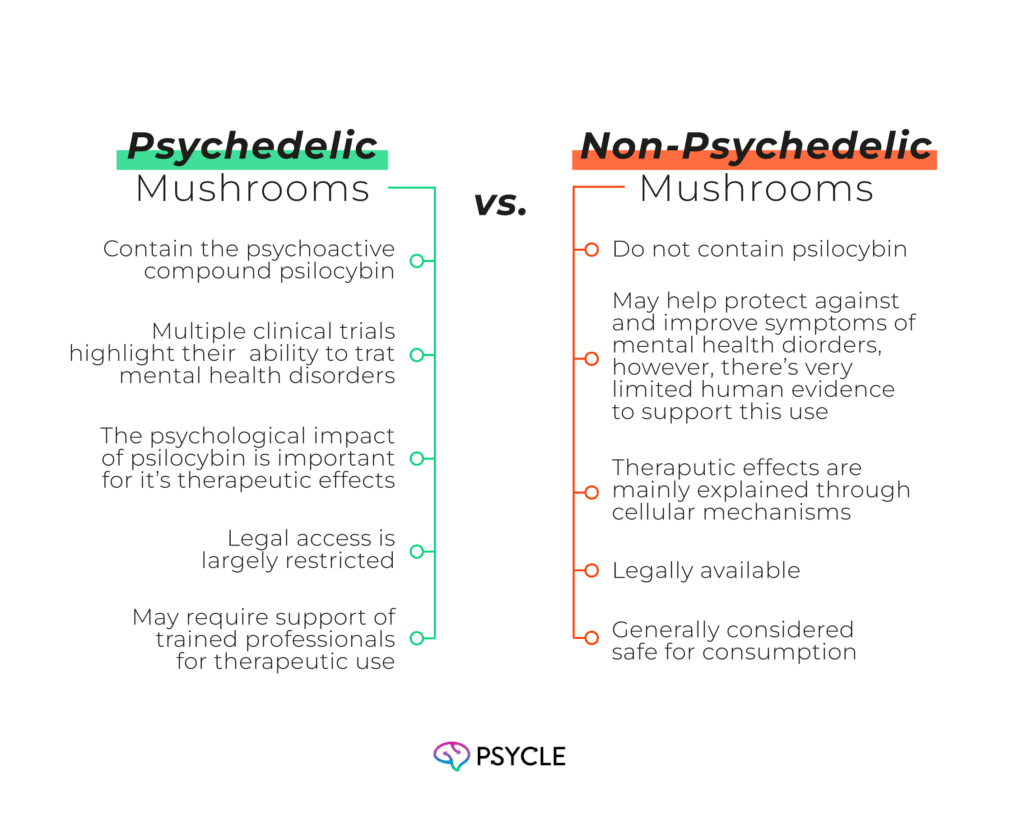
Comparative Table: Psychedelic vs. Non-Psychedelic Mushrooms
| Psychedelic Mushrooms | Non-Psychedelic Mushrooms |
| Contain the psychoactive compound psilocybin. | Do not contain psilocybin. |
| Multiple clinical trials highlight their ability to treat mental health disorders. | May help protect against and improve symptoms of mental health disorders, however, there’s very limited human evidence to support this use. |
| The psychological impact of psilocybin is important for it’s therapeutic effects. | Therapeutic effects are mainly explained though cellular mechanisms. |
| Legal access is largely restricted. | Legally available. |
| May require support of trained professionals for therapeutic use. | Generally considered safe for consumption. |
Conclusion
Both psychedelic and non-psychedelic mushrooms have shown promising benefits for mental health.
However, it is crucial to approach mushroom use, whether psychoactive or non-psychoactive, with caution. Safety, legality, and individual circumstances must be thoroughly considered before embarking on a psychedelic journey or integrating non-psychoactive mushrooms into a mental health regimen. It is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure the most suitable approach for individual needs.
As the field of mushroom research continues to expand, further studies are needed to fully grasp the implications and potential therapeutic applications of mushrooms for mental health. With ongoing research and careful consideration, mushrooms may play a significant role in enhancing mental well-being for many individuals.
FAQs
Are Mushrooms Good for Mental Health?
Research has shown a growing interest in the potential benefits of mushrooms for mental health, including improvements in mood and cognitive well-being.
What are the Effects of Magic Mushrooms on Mental Health?
Studies have shown that psilocybin, the psychedelic compound found in magic mushrooms, can provide significant relief from symptoms of major depressive disorder when combined with supportive psychotherapy. The effects can last up to a year.
What Mental Health Benefits Do Non-Psychedelic Mushrooms Have?
Non-psychedelic mushrooms like lion’s mane have been associated with anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects, reducing anxiety and depressive behaviors in animal studies. They have also been shown to decrease stress, improve sleep, regulate the immune system and improve neuroplasticity.
What is the Difference Between Psychedelic and Non-Psychedelic Mushrooms in Terms of Mental Health Benefits?
Psychedelic mushrooms have significant antidepressant effects, whereas non-psychedelic mushrooms have anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effects. The choice depends on individual preferences and therapeutic goals.
What Should I Consider Regarding Safety and Legality When It Comes to Mushrooms for Mental Health?
Psychedelic mushrooms are illegal in many countries and should only be used under the guidance of trained professionals in a research setting. Non-psychedelic mushrooms are generally safe for consumption but it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional.
What is the Future of Research on Mushrooms and Their Implications for Mental Health?
Further research is needed to explore the long-term efficacy and safety of mushrooms in treating various mental health disorders. This research has the potential to provide alternative options for individuals who have not found relief from traditional methods.
What are the Different Types and Varieties of Mushrooms?
Mushrooms come in various types and varieties, including magic mushrooms (psychedelic) and non-psychedelic mushrooms like lion’s mane and reishi.
How Can I Incorporate Mushrooms into My Lifestyle for Mental Health Benefits?
Mushrooms can be consumed in culinary dishes or as supplements. Psilocybin-assisted therapy can also be explored under the guidance of trained professionals where legal.
What are Some Personal Experiences and Testimonials Regarding Mushrooms for Mental Health?
Many individuals have reported positive experiences, including improvements in mood, cognition, and overall well-being. However, personal experiences may vary, and scientific research is ongoing.

