Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a powerful molecule that plays a vital role in maintaining health and the functioning of cells. In this article, we’ll explore the science behind NAD, how it affects the body, and its role in treating disease.
@makingitez Replying to @lakronksha what you know about that NAD! #NAD #longevity #justinbieber #haileybieber #ivtherapy #antiaging #biohacking
♬ original sound – Making it EZ
Key Takeaways
- NAD is a crucial molecule that powers energy production, supports DNA repair, regulates immune responses, and helps maintain cellular health, with declining levels linked to fatigue, inflammation, and age-related diseases.
- Supplementing with NAD precursors like NMN and NR, using injections or patches, and adopting lifestyle habits like exercise and intermittent fasting can help restore NAD levels and potentially slow signs of aging.
- While early research is promising, especially in animals, more human studies are needed to confirm long-term safety and effectiveness of NAD supplements in treating disease or extending lifespan.
What is NAD?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme, a type of helper molecule that works with enzymes to carry out important chemical reactions in the body. NAD is vital for energy production by regulating redox reactions, which involve the transfer of charges within cells.
In addition to producing energy, NAD activates enzymes that are involved in other essential cellular processes. This includes:
NAD plays an essential role in maintaining health and is, hence, a popular supplement for supporting overall well-being.
NAD and Energy Production
NAD exists in two forms: NAD+ (the oxidized form) and NADH (the reduced form). In simple terms, NAD+ grabs negatively charged electrons from nutrients like glucose, turning them into NADH. Electrons are then transferred to other proteins, which creates a charge that can be stored as energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Without enough NAD+, this energy-making process slows down, making it harder for cells to function properly.
When NAD+ levels drop too low, the body struggles to produce enough energy, which can contribute to fatigue and diseases related to metabolism. Conditions like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and fatty liver disease have been linked to low NAD+ levels.
Moreover, when energy production is disrupted, it can lead to the buildup of free radicals. These are unstable molecules that can damage important parts of the cell, including DNA and proteins. Over time, too many free radicals can contribute to aging and diseases.
Because of NAD’s role in energy, scientists have explored NAD supplements to help treat metabolic diseases and boost energy levels. Studies show that the therapeutic administration of NAD can increase metabolism in cells and decrease the production of free radicals. Some research indicates that drugs that enhance NAD can improve endurance during exercise.
However, these findings are mixed, and whether NAD supplements can directly impact exercise performance is unclear.
NAD and DNA Repair
NAD is crucial for maintaining the health of our DNA. DNA can be damaged by everyday activities like exposure to sunlight, environmental toxins, and even normal cellular processes. If this damage isn’t fixed, it can lead to mutations that cause abnormal proteins to form. This can cause cells to become dysfunctional, harm other cells, and eventually lead to diseases, including cancer.
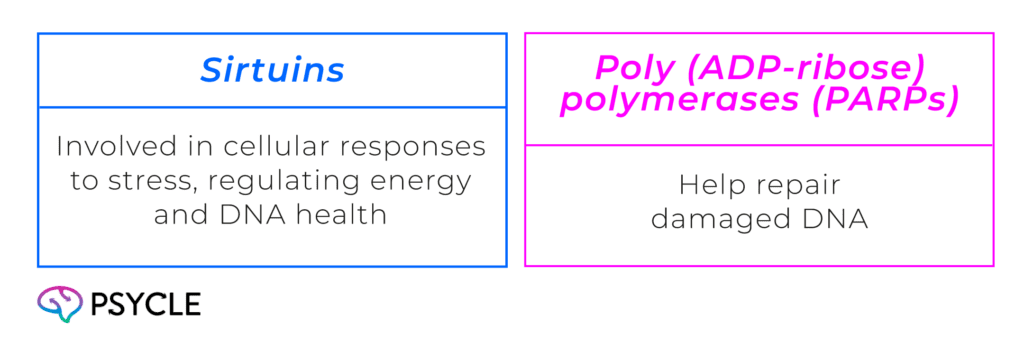
NAD helps activate PARPs and sirtuins, which are essential for detecting and repairing DNA damage. When DNA is harmed, PARPs use NAD to signal repair mechanisms, while sirtuins help maintain the structure and stability of our genetic material. By supporting these proteins, NAD⁺ ensures that our DNA remains intact and functions properly.
Keeping our DNA stable is vital because unstable DNA is linked to various diseases. Some animal studies show that NAD supplementation could help prevent cancer and reduce the spread of tumors. However, NAD may also encourage tumour growth by boosting energy production in cancer cells and other mechanisms.
One study showed that NAD supplementation recovered DNA damage related to Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) in mice. The treated mice showed improved measures of DNA health connectivity in the brain and motor and cognitive function compared to untreated mice.
NAD Role in Immunity
The immune system is the body’s natural defense system that helps fight harmful microorganisms. While the immune system is vital for protecting against infections, excessive inflammation can damage tissues and result in diseases.
NAD helps regulate the immune system by activating sirtuins that inhibit proteins involved in the inflammatory response. Keeping DNA healthy also prevents the immune system from being triggered by mutated proteins.
Research indicates that boosting NAD levels can help manage inflammatory diseases. For instance, mice experiments show improved inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) symptoms following treatments that increase NAD.
How Does NAD Affect Aging?
As we grow older, our NAD levels naturally decrease. This decline is due to several factors, including reduced production of NAD and increased consumption by certain enzymes. For instance, the enzyme CD38, which breaks down NAD, becomes more active with age, leading to lower NAD levels.
Lower NAD levels can affect many vital functions in the body, increasing the risk of age-related diseases. Research suggests that raising NAD levels may help slow down certain health issues relating to aging, including cognitive decline. Animal studies have even shown that boosting NAD can extend lifespan. However, more research is needed to understand how safe and effective NAD supplements are at reducing human aging.
Strategies to Boost NAD
Supplementation with NAD⁺ Precursors
One approach to increasing NAD⁺ levels is to supplement with its precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). These compounds are converted into NAD within the body, potentially enhancing its availability.
Lifestyle Interventions
In addition to supplementation, certain lifestyle modifications may help maintain or boost NAD⁺ levels:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has been associated with increased NAD⁺ levels and enhanced activity of NAD-dependent enzymes, such as sirtuins.
- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating foods rich in NAD precursors, such as tryptophan-containing foods (e.g., turkey, nuts, seeds) and niacin (vitamin B3) sources (e.g., meat, fish, whole grains), may support NAD biosynthesis. Additionally, certain dietary patterns, like intermittent fasting or caloric restriction, have been linked to increased NAD levels and activation of NAD-dependent enzymes, potentially promoting longevity and metabolic health.
NAD Injections
NAD injections are becoming increasingly popular for individuals seeking more immediate or concentrated results. These injections direct the molecule into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system and providing a quick increase in NAD levels.
NAD Patches
Another method that is gaining traction is the use of NAD patches. These transdermal patches are designed to deliver NAD through the skin over a period of time, allowing for a steady absorption of the molecule. Patches are less invasive and more convenient than injections.
Considerations and Future Directions
NAD plays a vital role in many essential bodily functions, including energy production, DNA repair, immune regulation, and cellular health.
Evidence suggests that boosting NAD levels may help improve metabolic health, support immune function, treat disease, and even slow aging. However, much of the research conducted so far has been in animals, so the effectiveness and safety of NAD supplementation, especially in the long term, remain uncertain.
If you’re considering using NAD⁺ supplements, whether in the form of precursors, injections, or patches, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional first. A healthcare provider can help evaluate your specific health needs and advise you on the safest and most effective course of action.
As science progresses, future studies will hopefully provide clearer answers on how best to utilize NAD to enhance health and treat disease.
FAQs
Are There Side Effects of NAD?
While NAD supplementation is generally considered safe, there may be some side effects, particularly with high doses. Some people have reported mild symptoms like headaches, nausea, or digestive discomfort. As with any supplement, it’s essential to start with a lower dose and consult a healthcare provider before making changes, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions.
Why Do People Supplement with NAD?
People use NAD for many reasons. Some people find it helps boost energy levels, improve mental clarity, and reduce fatigue. It’s also used to help with weight management because of its metabolic effects. People mostly use NAD supplements to promote overall health.
Sources
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7963035/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37971292/

