Ketamine offers hope to those in crisis, with a powerful ability to reduce thoughts about suicide. This article delves into the effects of ketamine on suicidal ideation, exploring its mechanisms, treatment models, and the safety considerations associated with its use.
Key Takeaways
- Ketamine can significantly reduce suicidal thoughts within hours, making it a vital option for those at risk.
- There are two main approaches to ketamine treatment: clinical infusions (intravenous or intranasal) and Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy (KAP), each with unique benefits.
- Studies have shown a high percentage of participants experience remission from suicidal thoughts after ketamine treatment, particularly with repeated doses.
- While generally safe, ketamine can cause side effects like dizziness, dissociation, and increased blood pressure, warranting careful monitoring.
- Long-term effects of repeated ketamine use are still being studied, and individuals with certain health conditions or substance abuse issues should approach treatment cautiously.
Prevalence of Suicidal Ideation and Its Impact
Suicide remains one of the biggest mental health challenges worldwide. In the United States alone, over 40,000 people die by suicide each year, with trend data showing these figures are continuing to rise.
Suicidal ideation (SI) refers to thoughts about ending one’s life. These thoughts can be brief or involve detailed planning. For people experiencing SI, it often brings overwhelming sadness and a profound sense of isolation, making daily life difficult.
SI doesn’t only affect the person struggling with these thoughts. Friends and family may experience helplessness, anxiety, and emotional exhaustion, knowing that a loved one may end their life. People with SI might not tell their friends and family about their ideation to protect them. However, this can deepen the person’s loneliness and worsen their mental health.
SI can be caused by many things, but it is commonly linked to stressful life events and mental health conditions, most notably treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Those with TRD may feel particularly hopeless with a persistent depression that can’t be alleviated with available treatments. Suicide may feel like the “only way out” of depressive thoughts and feelings.
Ketamine’s Rapid Reduction of Suicidal Ideation
Ketamine was originally developed as an anesthetic, but it has recently gained attention as a promising treatment for depression. Unlike traditional antidepressants that can take weeks to work, ketamine’s antidepressant effects can occur within hours after treatment.
One of the standout benefits of ketamine is its ability to significantly rapidly reduce SI, with research showing that ketamine can alleviate SI within hours after an infusion. These quick effects are particularly important for individuals who are at risk of suicide, making ketamine a potential lifesaver.
In addition to its fast action, ketamine also provides lasting benefits. Studies indicate that it can continue to reduce suicidal thoughts for up to 72 hours after the infusion. This period can give individuals the time they need to start exploring other therapeutic options and take steps toward improving their mental health.
Mechanisms of Action and Brain Chemistry
Ketamine works differently from traditional antidepressants. It targets specific proteins called NMDA receptors, which increase the activity of glutamate, a key chemical messenger in the brain. This boost in glutamate activity enhances function in the prefrontal cortex, an area associated with mood and decision-making.
Additionally, ketamine promotes neuroplasticity, which is the brain’s ability to form and repair connections. This process can help strengthen neural pathways that may have been damaged by stress or depression. By combining these neuroplastic effects with therapy, patients may be more able to develop healthier habits and gain new perspectives on their lives.
Research indicates that ketamine’s ability to reduce suicidal thoughts may occur through different mechanisms than its antidepressant effects. However, since it can help alleviate depression, especially in those who have not responded to other treatments, ketamine plays a valuable role in suicide prevention. Long-term treatment plans that incorporate ketamine along with therapy can be especially beneficial.
Ketamine Treatment for Suicidal Ideation
Ketamine treatment for suicidal ideation is available through various approaches, primarily falling into two categories: a clinical model and Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy (KAP).
In the clinical model, ketamine is administered through intravenous (IV) infusions, intranasal spray, or intramuscular injections, typically in specialized clinics. IV infusions are the most researched method for reducing suicidality and may be best for those feeling close to suicide since they have the most rapid effects.
Intranasal ketamine in clinical settings tends to come in the form of Spravato (esketamine). The drug contains one of ketamine’s two chemical components and was approved by the FDA for both TRD and major depressive disorder (MDD) with suicidal ideation in 2019. Because of its approval, Spravato tends to be more affordable than IV ketamine, as it’s more widely covered by insurance.
To date, there’s very little option to get help for suicide in an emergency department setting. However, health experts have proposed ketamine could be a safe and effective option for those in need of rapid relief in the ED.
Ketamine-assisted psychotherapy (KAP), on the other hand, is a much longer approach but could give rise to sustained life changes that prevent suicidal thoughts from reoccurring. This approach combines ketamine–often through lozenges or sublingual tablets—with therapeutic sessions. Ketamine is used to help facilitate emotional processing and exploration, allowing patients to work through trauma and difficult feelings in a supportive environment.
Real-World Evidence of Ketamine’s Efficacy
In a study involving 156 participants, researchers compared the effects of two intravenous infusions of ketamine to a placebo on suicidal ideation over three days. Results showed that 63.0% of those receiving ketamine achieved full remission, compared to 31.6% in the placebo group.
They found the effect was more pronounced in participants with bipolar disorder compared to MDD. The participants also had minimal side effects, with no manic or psychotic symptoms reported.
Meta-Analysis and Network Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to identify the outcomes of a treatment or answer to a specific research question. One of these analyses investigated ten studies with 167 participants and found that ketamine significantly reduced suicidal ideation within just one day after treatment. The effects were strong, showing improvements in clinician-judged assessments and self-reported feelings.
A network meta-analysis compares multiple treatment and treatment methods across different studies. One network meta-analysis of ketamine for SI found that participants who received ketamine had a much greater reduction in suicidal thoughts compared to those who received a control drug. They also showed that when participants received repeated doses of ketamine, their improvement in suicidal thoughts after the last dose was significantly better than after the first dose.
Though these findings are promising, the studies investigating ketamine for SI have been criticized. For example, in a British Medical Journal article, the authors pointed out that suicidal risk was often poorly measured and that most studies measured the response as a 50% reduced SI score, as opposed to the complete absence of suicidal ideas. Moreover, they noted that the sample sizes were relatively small.
Safety and Side Effects of Ketamine Treatment
Ketamine is generally considered safe when administered under medical supervision, but like any medication, it can have side effects. Common side effects of ketamine include:
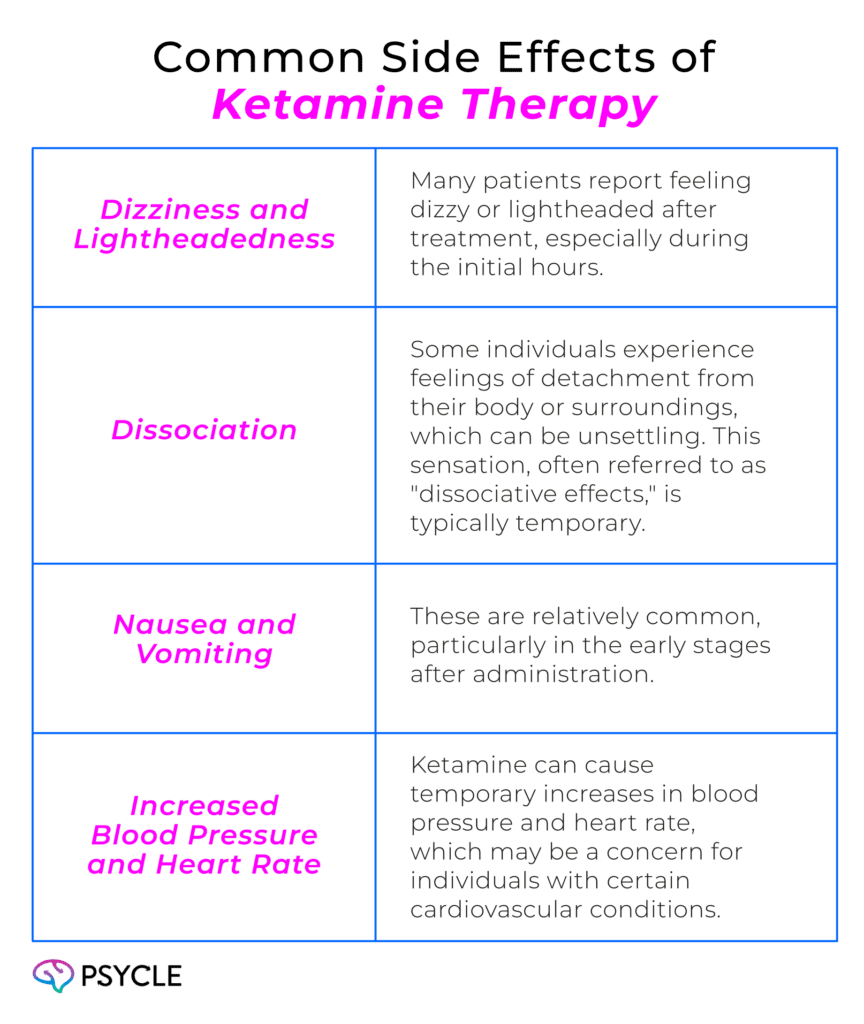
Most side effects are short-lived and tend to resolve within hours after the infusion. However, ongoing monitoring during and after treatment is important to manage any adverse effects.
In terms of long-term safety, the data on repeated ketamine use is still evolving. While some studies suggest it may be safe for multiple treatments, there is a need for more long-term research into the effects of repeated ketamine treatments over several years.
Ketamine can also be addictive, so it is recommended not to be used by those with an ongoing substance abuse disorder.
FAQs
What is the Average Cost of Ketamine Treatment?
The cost of ketamine treatment can vary widely depending on the method of administration, the clinic, and your location. Generally, individual infusions can range from $400 to $800 each. Some insurance companies may be able to cover costs, but these options are generally limited.
What Side Effects Might I Experience with Ketamine Treatment?
Common side effects include dizziness, feelings of detachment (dissociation), nausea, and temporary increases in blood pressure. Most side effects are short-lived and resolve within hours.
How Quickly Does Ketamine Work for Suicidal Ideation?
Ketamine can start to alleviate suicidal thoughts within hours after administration, making it an important option for individuals in crisis.

