When it comes to therapy choices for mental health, two approaches that often come up are Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT). While they both aim to improve mental well-being, they have distinct differences in their focus and techniques.
Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions about the most suitable treatment for individuals.
Key Takeaways
- CBT and DBT are two therapeutic approaches with unique focuses and techniques.
- CBT emphasizes thoughts and behaviors, while DBT emphasizes emotional regulation and acceptance strategies.
- CBT is effective for conditions such as depression, anxiety, OCD, phobias, and PTSD.
- DBT is particularly suited for borderline personality disorder, self-harming behaviors, and chronic suicidal ideation.
- Both CBT and DBT have shown effectiveness in improving mental health outcomes.
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a highly effective form of psychological treatment widely used for various mental health conditions. It has shown significant effectiveness in treating depression, anxiety disorders, addiction, eating disorders, and severe mental illness.
Numerous research studies have demonstrated the positive outcomes and improvements in functioning and quality of life achieved through CBT.
The core principle of CBT is based on the understanding that psychological problems arise from faulty thinking patterns and learned cycles of unhelpful behavior. By addressing these underlying factors, CBT aims to bring about lasting positive change and empower individuals to regain control over their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
CBT involves a collaborative process between the therapist and the individual seeking treatment. The therapist guides the individual through exercises and homework assignments that challenge and modify their unproductive thought patterns.
This process helps individuals develop more adaptive and realistic thinking styles, leading to healthier behaviors and improved mental well-being.
The structured nature of CBT ensures that treatment is focused and goal-oriented. Sessions are typically short-term and time-limited, providing individuals with practical tools and strategies that they can apply to their everyday lives.
Research studies consistently highlight the effectiveness of CBT in producing positive outcomes across a range of mental health conditions. It is a widely recommended and evidence-based treatment option that has proven its efficacy over time.
The research-backed effectiveness of CBT makes it a popular choice among mental health professionals and individuals seeking psychological treatment.
What is Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)?
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a form of talk therapy adapted from Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) specifically designed for individuals experiencing intense emotions.
Developed by Marsha Linehan in the 1970s, DBT emphasizes acceptance of reality and teaches coping mechanisms to enhance emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness.
Unlike CBT, DBT recognizes the significance of emotions in mental well-being. It equips individuals with the necessary skills to navigate and manage their emotions effectively, allowing them to lead a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Through a collaborative therapeutic process, DBT helps individuals understand their emotions and develop healthy coping mechanisms. It encourages acceptance of oneself and promotes the exploration of effective ways to regulate emotions, improve interpersonal relationships, and navigate distressing situations.
Key Components of CBT and DBT
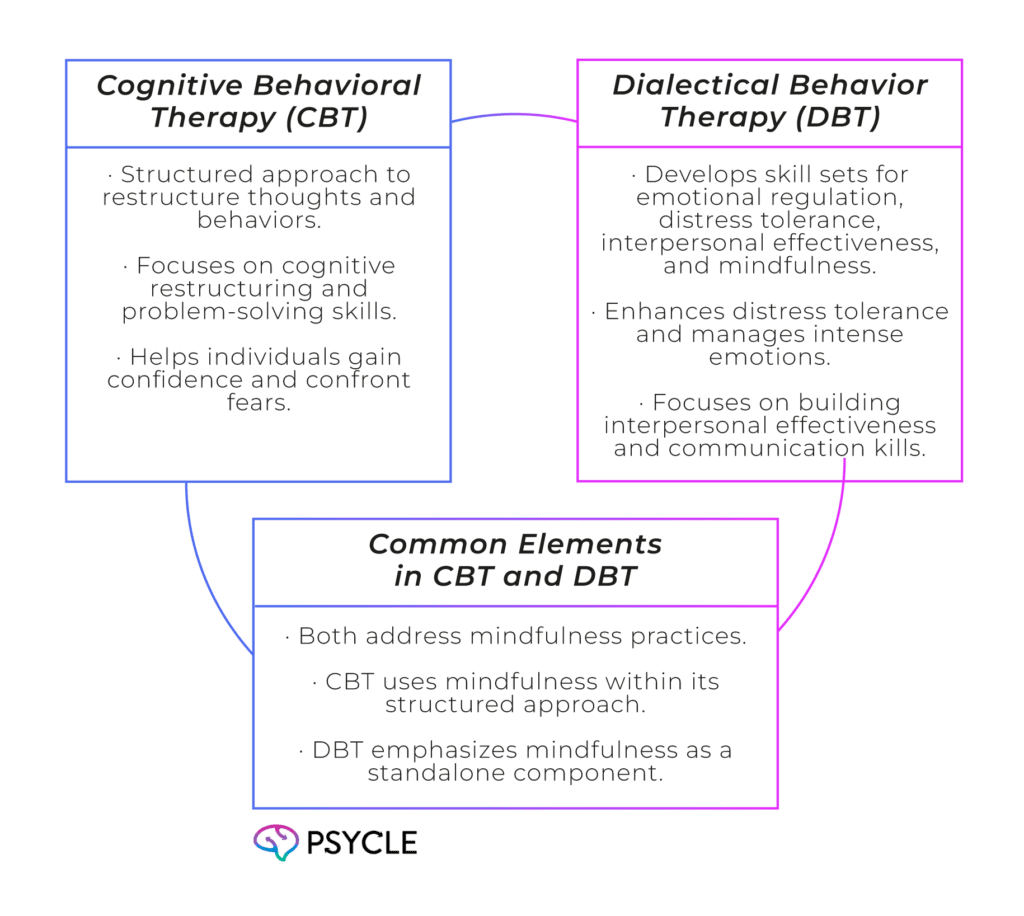
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) use different techniques to address different aspects of mental health. CBT employs a structured approach to restructure thoughts and behaviors, while DBT focuses on developing skill sets for emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness.
CBT involves recognizing distortions in thinking and utilizing cognitive restructuring techniques to challenge and change negative thought patterns. Individuals undergoing CBT learn problem-solving skills to address challenges, gain confidence in their abilities, and confront their fears.
On the other hand, DBT emphasizes enhancing important skill sets for emotional regulation. It helps individuals improve distress tolerance, manage intense emotions, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
DBT also focuses on building interpersonal effectiveness, helping individuals navigate relationships, and communicating effectively.
Mindfulness is a key component addressed in both CBT and DBT. While CBT utilizes mindfulness as a tool within the structured approach, DBT places particular emphasis on it as a standalone component. Mindfulness practices help individuals cultivate present-moment awareness, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
Techniques Used in CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) employs a variety of techniques to help individuals overcome their psychological challenges and improve their overall well-being. These techniques are designed to target specific areas such as cognitive restructuring, problem-solving skills, confidence-building, and exposure therapy.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is a fundamental technique in CBT that involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns. By recognizing and reframing distorted thoughts, individuals can develop a more balanced and realistic outlook on themselves and their life situations.
This technique is particularly useful for addressing issues such as anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Problem-Solving Skills
CBT also places a strong emphasis on developing problem-solving skills. This technique helps individuals learn practical strategies to effectively tackle challenges and overcome obstacles in their daily lives.
By enhancing problem-solving abilities, individuals can become more proactive in resolving issues and achieving their goals.
Confidence-Building
Building confidence is another important aspect of CBT. Therapists work with individuals to identify their strengths, challenge self-doubt, and cultivate a positive self-image.
By developing self-confidence, individuals can improve their overall well-being and approach life’s challenges with resilience and optimism.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a technique used in CBT to help individuals confront and overcome their fears and phobias. By gradually exposing individuals to the situations or stimuli that trigger their anxiety or distress, they can learn effective coping mechanisms and reduce avoidance behaviors.
This technique has proven to be highly effective in treating anxiety disorders, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Techniques Used in DBT
DBT incorporates a variety of techniques to help individuals navigate their emotions, develop healthier coping mechanisms, and improve their interpersonal relationships. These techniques are specifically designed to address emotional regulation, distress tolerance, mindfulness, and interpersonal effectiveness.
Mindfulness
One of the key techniques used in DBT is mindfulness. Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, observing thoughts and emotions without judgment or attachment. By cultivating mindfulness, individuals can develop a greater awareness of their internal experiences and learn to respond to them in a more balanced and grounded manner.
Emotional Regulation
DBT also focuses on teaching individuals skills for emotional regulation. This involves learning to identify, understand, and manage intense emotions in a healthy and adaptive way. By gaining skills in emotional regulation, individuals can minimize impulsive and destructive behaviors often associated with emotional dysregulation.
Distress Tolerance
Another crucial element of DBT is distress tolerance. This technique helps individuals cope with distressing situations and emotions by developing effective strategies for managing and tolerating distress. By increasing distress tolerance, individuals can navigate challenging situations without resorting to harmful behaviors or feeling overwhelmed.
Interpersonal Effectiveness
DBT places significant emphasis on improving interpersonal effectiveness, as healthy interpersonal relationships are vital for overall well-being. This technique involves developing skills such as assertiveness, active listening, and conflict resolution to enhance communication and build healthier relationships with others.
By employing these techniques, DBT has been shown to be effective in helping individuals manage intense emotions, cope with challenging situations, and improve their overall quality of life.
Outcome Goals in CBT and DBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) have distinct outcome goals that reflect their unique approaches to therapy. Both CBT and DBT aim to improve individuals’ mental health and well-being, but they prioritize different areas of focus.
CBT: Problem-Solving and Realistic Outlook
In CBT, the outcome goals revolve around problem-solving and developing a more realistic outlook on life. By working with a therapist, individuals learn strategies to identify and challenge negative thought patterns, which can contribute to emotional distress and maladaptive behaviors.
CBT helps individuals develop effective problem-solving skills, allowing them to approach challenges with a more rational mindset. The ultimate objective of CBT is to improve overall functioning and enhance the quality of life for individuals experiencing mental health difficulties.
DBT: Emotional Balance and Healthy Coping Mechanisms
On the other hand, the outcome goals in DBT center around achieving emotional balance and developing healthy coping mechanisms. DBT acknowledges that emotions play a significant role in individuals’ lives and that problems often arise from difficulty regulating intense emotions.
Through DBT, individuals learn strategies for emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. The aim is to empower individuals to effectively manage their emotions, navigate challenging situations, and improve their relationships with others.
DBT seeks to foster a balanced and fulfilling life for individuals struggling with emotional dysregulation.
While CBT and DBT share the common goal of improving mental health, they prioritize distinct aspects of well-being.
Whether an individual is seeking problem-solving skills and a realistic outlook on life (CBT) or aims to achieve emotional balance and healthy coping mechanisms (DBT), both therapies offer valuable tools and techniques to support individuals on their journey towards improved mental well-being.
Suitability of CBT and DBT for Mental Health Conditions
When it comes to treating mental health conditions, both Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) have proven to be effective approaches. However, their suitability varies depending on the specific condition being addressed.
CBT is widely used and has shown effectiveness in treating various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, obsessive compulsive disorder, addiction, eating disorders, phobias, marital problems, and PTSD. For example, CBT can treat:
Anxiety: CBT can help individuals with anxiety disorders by identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety. It also focuses on developing coping skills to manage anxiety symptoms.
Depression: CBT is an evidence-based therapy for depression. It helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their depressive symptoms. Through CBT, individuals can learn effective problem-solving skills and develop healthier ways of thinking. DBT, on the other hand, is particularly suited for borderline personality disorder, self-harming behaviors, and chronic suicidal ideation.
For example, DBT can treat:
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): DBT is considered the gold standard treatment for BPD. It helps individuals regulate their emotions, manage impulsive behaviors, and improve their interpersonal skills. Through a combination of individual therapy, group skills training, and phone coaching, DBT provides a comprehensive approach to managing BPD symptoms.
Self-Harming Behaviors: DBT is particularly effective in addressing self-harming behaviors such as cutting and suicidal ideation. It teaches individuals distress tolerance skills, emotion regulation techniques, and alternative coping strategies to reduce self-destructive behaviors.
Chronic Suicidal Ideation: DBT provides individuals with tools to manage chronic suicidal thoughts and behaviors. By learning effective coping strategies, individuals can develop a greater sense of control over their emotions and reduce the intensity of their suicidal ideation.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of CBT and DBT extends beyond the mentioned conditions, as they can be adapted to address a wide range of mental health concerns. The choice between the two therapies depends on the individual’s needs, preferences, and the expertise of the therapist. It is advisable to consult with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate therapeutic approach for individual needs.
Conclusion
CBT and DBT are two distinct therapeutic approaches that offer valuable treatment choices for individuals with mental health conditions. Understanding the differences between these therapeutic approaches can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options.
CBT, or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, focuses on thoughts and behaviors. It is a structured approach that involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, problem-solving, and building confidence. CBT has proven effective for a range of conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, addiction, and eating disorders.
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, emphasizes emotional regulation and acceptance strategies. It teaches skills for distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. Developed by Marsha Linehan, DBT is particularly suited for conditions like borderline personality disorder, self-harming behaviors, and chronic suicidal ideation.
Both CBT and DBT have shown effectiveness in improving mental health outcomes. The choice between these therapeutic approaches depends on individual needs and preferences. Overall, CBT and DBT provide valuable treatment choices for individuals seeking to improve their mental health and well-being.
FAQs
Are CBT and DBT Effective Therapeutic Approaches?
Yes, both CBT and DBT have shown effectiveness in improving mental health outcomes for individuals.
Can CBT and DBT Be Used Together?
Yes, CBT and DBT can be used together in some cases, with therapists tailoring the treatment approach to meet the individual’s needs.
What Applications Are CBT and DBT Commonly Used For?
CBT is commonly used for anxiety disorders, depression, addiction, eating disorders, and marital problems. DBT is particularly effective for borderline personality disorder, self-harming behaviors, and chronic suicidal ideation.