Ibogaine is a psychedelic compound derived from a West African plant that has powerful effects on the brain. In this article, we’ll explore how ibogaine works, what science says about its effects, and why researchers are so interested in its potential.
Key Takeaways
- Ibogaine is a natural compound found in the Tabernanthe iboga plant.
- It has been traditionally used by the Bwiti people in spiritual and healing ceremonies.
- Studies suggest ibogaine can help treat addiction and other neurological disorders.
- It influences brain chemistry by promoting the action of growth factors and chemical messengers and enhancing energy production.
- Research into ibogaine’s effects is ongoing, with scientists exploring new ways to harness its benefits safely.
What is Ibogaine?
Ibogaine is a psychoactive compound derived from the Tabernanthe iboga plant, which is native to West Africa. For centuries, the Bwiti people of Gabon have used iboga in initiation and healing ceremonies. They see it as a sacred plant that provides deep insight and healing.
French researchers first isolated Ibogaine in the early 20th century and initially marketed it as a stimulant. Its potential as an addiction treatment was later discovered by pharmacologist Howard Lotsof.
Today, ibogaine therapy for addiction–particularly opiate addiction–is widely recognized, and treatment centers have opened across the globe. However, due to its psychedelic effects and potential heart risks, ibogaine remains a Schedule I drug in most countries and is only legally available in a few places.
As well as substance use, ibogaine has shown promise in treating several other conditions. Clinical studies show it can relieve symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and brain injuries. Clinics also provide ibogaine for mood disorders like depression and anxiety, and patients report profound therapeutic benefits.
The Neuroscience of Ibogaine
The neuroscience of ibogaine is complex. It doesn’t just affect one system but influences multiple different chemicals and pathways, leading to various therapeutic effects.
Ibogaine Increases the Expression of Neurotrophic Factors
Neurotrophic factors are proteins that help brain cells grow, survive, and repair themselves.
Studies show that ibogaine increases levels of several key neurotrophic factors:
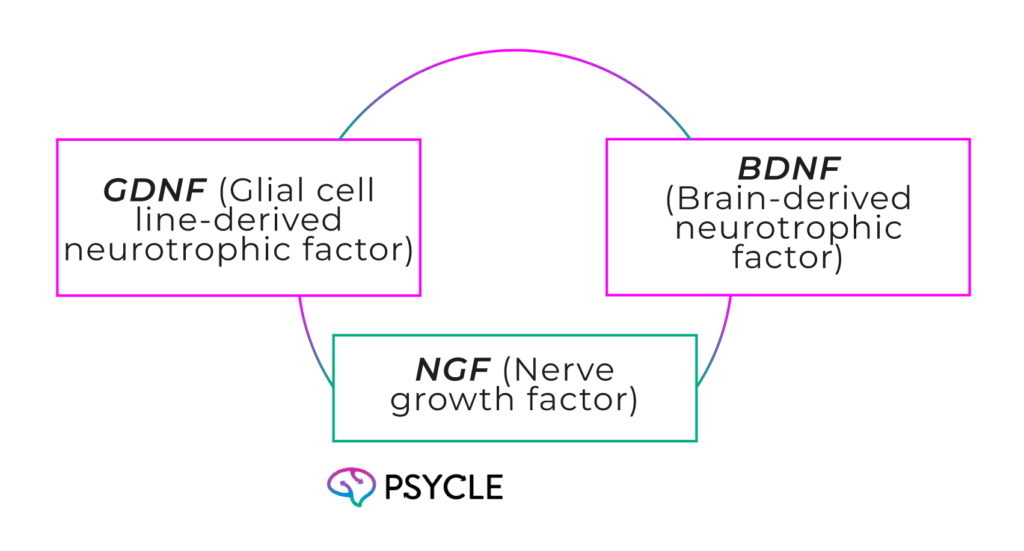
Neurotrophic factors help explain why ibogaine helps with recovery from traumatic brain injury and repair cells that are damaged by addiction disorders. BDNF also plays an essential role in synaptic plasticity, which could explain ibogaine’s benefits for mental health.
Synaptic plasticity is the process by which the brain can change and form connections between nerve cells, which may increase people’s capacity to relearn negative thoughts and behavior patterns.
Ibogaine Increases Energy Production in Cells
At a cellular level, ibogaine enhances the way cells produce energy. Studies show that ibogaine boosts the genetic expression of enzymes involved in:
- Glycolysis – The process of breaking down glucose for energy.
- The TCA (tricarboxylic acid) cycle – A key part of cellular respiration that generates ATP, the body’s energy currency.
Additionally, ibogaine makes energy production more efficient, lowering the amount of baseline ATP needed to maintain essential “housekeeping” functions.
Ibogaine Reduces Damage Caused by Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress happens when harmful molecules called free radicals damage cells, including neurons. This can contribute to aging and neurological diseases.
Ibogaine helps combat oxidative stress by:
- Improving metabolic efficiency and reducing the number of free radicals produced.
- Increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, which help neutralize harmful molecules.
This protective effect may explain why ibogaine has potential benefits for neurodegenerative conditions.
Ibogaine Increases Dopamine and Serotonin at Synapses
Dopamine and serotonin are neurotransmitters that regulate mood, motivation, and reward, and ibogaine affects these systems in two key ways:
- Blocks the reabsorption of dopamine and serotonin – This means more of these “feel-good” chemicals remain in the brain, explaining the mood-boosting effects of ibogaine.
- Helps fix misfolded transporter proteins – This may improve neurotransmitter function over time, enhancing brain health and resilience.
Dopamine plays a key role in the brain’s reward system, reinforcing behaviors that bring pleasure or relief. In addiction disorders, repeated substance use disrupts dopamine signaling, leading to lower natural dopamine production and reduced sensitivity to rewards.
This makes it harder for individuals to feel pleasure from everyday activities, driving compulsive drug-seeking behavior to compensate. By restoring dopamine function, ibogaine can help reduce cravings and drug-seeking behavior, making it easier for individuals to break free from addiction.
Ibogaine Modifies Functional Connectivity
Functional connectivity (FC) refers to how different parts of the brain communicate with each other. Studies show that ibogaine can change the coordinated firing of neurons, altering FC and potentially explaining changes in people’s perception and thought patterns.
This is likely responsible for its psychedelic effects and could explain why many users report profound psychological insights. FC could also explain how ibogaine helps people break free from negative thought patterns.
The Future of Ibogaine Research
While we’re beginning to understand how ibogaine affects the brain, the whole picture is still unclear. Many studies have been conducted on isolated cells or mice, so their findings may not fully reflect how ibogaine works in real life.
However, an increasing number of studies and case reports show that ibogaine has positive outcomes on human patients.
Despite its promise, ibogaine is not without risks. It has been associated with potential heart complications, and its psychedelic effects can be intense. Scientists are working to develop safer alternatives that retain ibogaine’s beneficial effects while minimizing risks.
A major area of interest is creating ibogaine-derived compounds that:
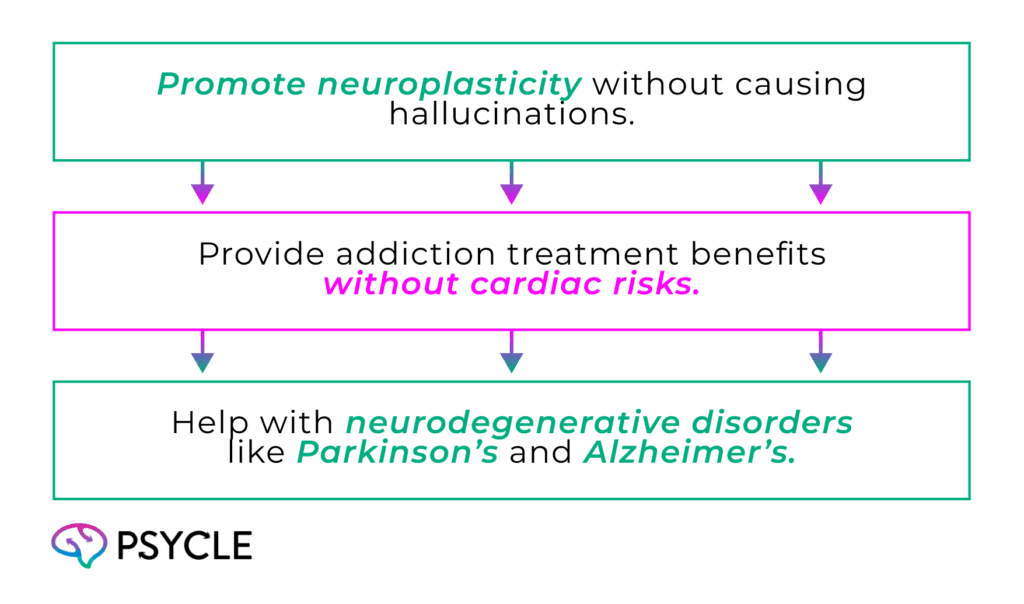
As research continues, ibogaine may open new doors for treating addiction, depression, and brain disorders.
Final Words
Ibogaine is a fascinating compound with powerful effects on the brain. Its therapeutic potential is vast, from promoting neuroplasticity to enhancing energy production and mood regulation.
However, more research is needed to fully understand its risks and benefits. As scientists continue to explore ibogaine and its derivatives, we may soon see new, safer treatments inspired by this remarkable natural substance.
FAQs
Can Ibogaine Cure Depression?
Ibogaine shows promise in treating depression, but it is not a guaranteed cure. Studies suggest it boosts serotonin and neurotrophic factors, improving mood and brain function. However, its effects vary, and more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness.
What Are the Risks of Ibogaine?
While ibogaine has potential benefits, it also carries risks, including:
- Cardiotoxicity – It can affect heart rhythms, leading to potential complications.
- Intense psychedelic effects – Some users experience distressing hallucinations.
- Neurological risks – In high doses, ibogaine can be neurotoxic.
Due to these risks, ibogaine should only be used under medical supervision in a controlled setting.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30471681/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0740547221004438
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7882011/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33299186/

